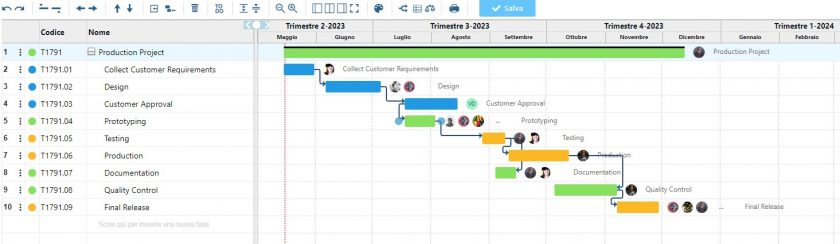
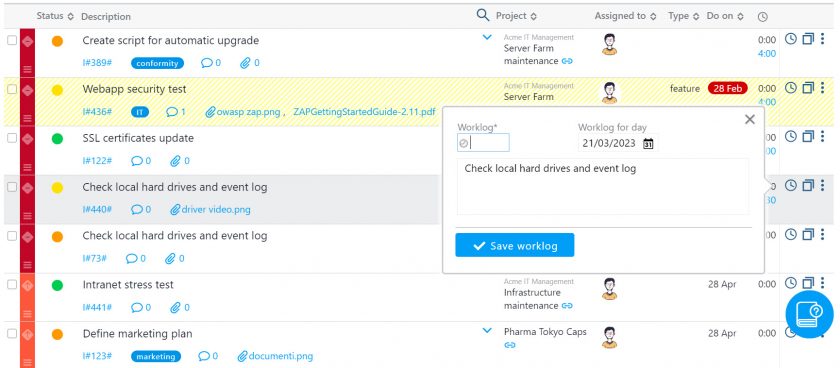
Would you like to learn more about all the methods and tools that Twproject offers you for effective and profitable portfolio management? Here you will find lots of useful information and also some tips to put into practice.
CONTENT
Portfolio Management is a type of broader strategic management that deals with evaluating projects as a whole and the organisation’s ability to execute them.
In today’s increasingly dynamic and demanding environment, the role of the Portfolio Manager, a distinct position from the Project Manager, is crucial. The task of the Portfolio Manager is to hold the ranks together and help companies evolve and achieve their strategic objectives.
Aims and objectives of Portfolio Management
Let us start with a definition: when we talk about Portfolio Management, we mean the coordinated management of several corporate projects, done for various strategic purposes.
Project portfolio management can in fact have various objectives and purposes, and they are:
- Having an overview of all projects and categories of projects (or programmes), in order to assess business efficiency, return on investment (ROI) and the direction towards specific innovation choices.
- Achieving greater transparency on corporate objectives and resource management and being able to share this data internally and externally (teams and stakeholders)
- Ensuring that the allocation of resources (human resources, but also assets, materials and services) is always optimal and in line with corporate planning strategies.
- Providing information on the financial viability of projects, so as to highlight the lines on which to make the right investments in the future.
- Guaranteeing that the relevance of projects is periodically analysed and modified as necessary, so that time and resources are invested accordingly.

Twproject has an optimal solution for all these goals and provides you with various tools for portfolio management.
Let us take a look at the main tools it provides.
Performing good Portfolio Management with Twproject
In Portfolio Management, Twproject provides very useful tools and methodologies to coordinate and clearly define the work of the whole team.
Generally speaking, it aims at linking day-to-day work with strategic corporate objectives, helping define an action plan.
In ths section we will see what areas to consider when carrying out this activity and how we can make use of Twproject’s functionalities.
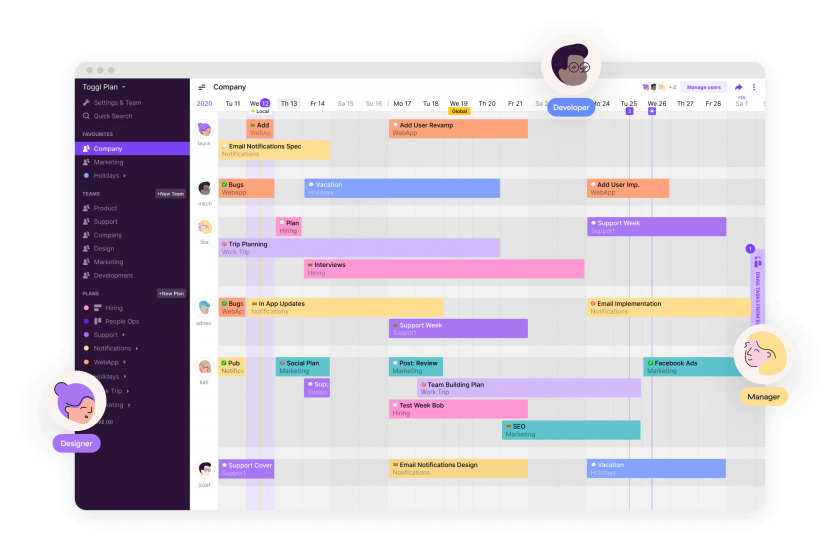
Overview of any planning issue
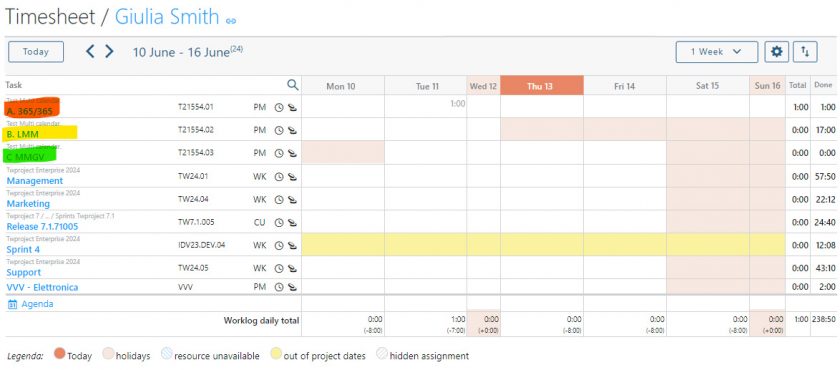
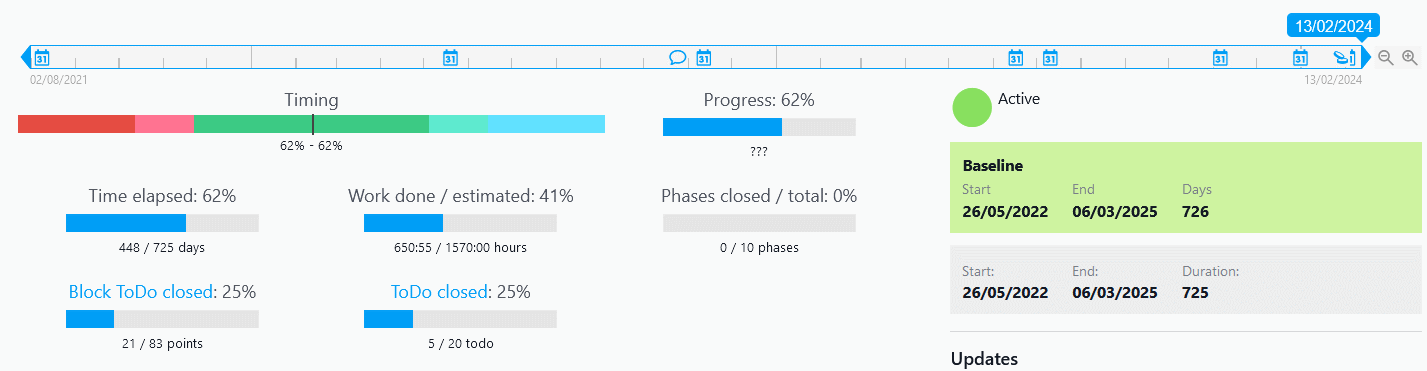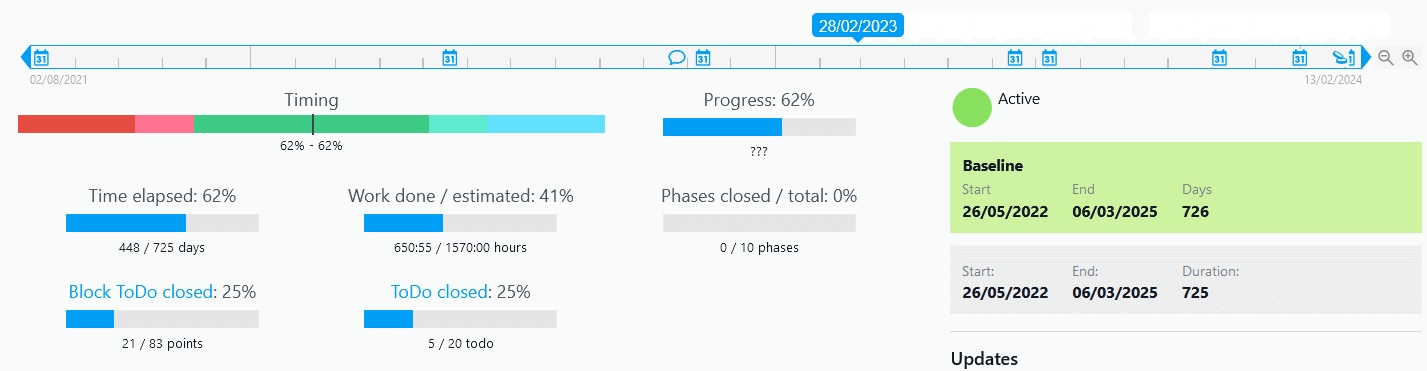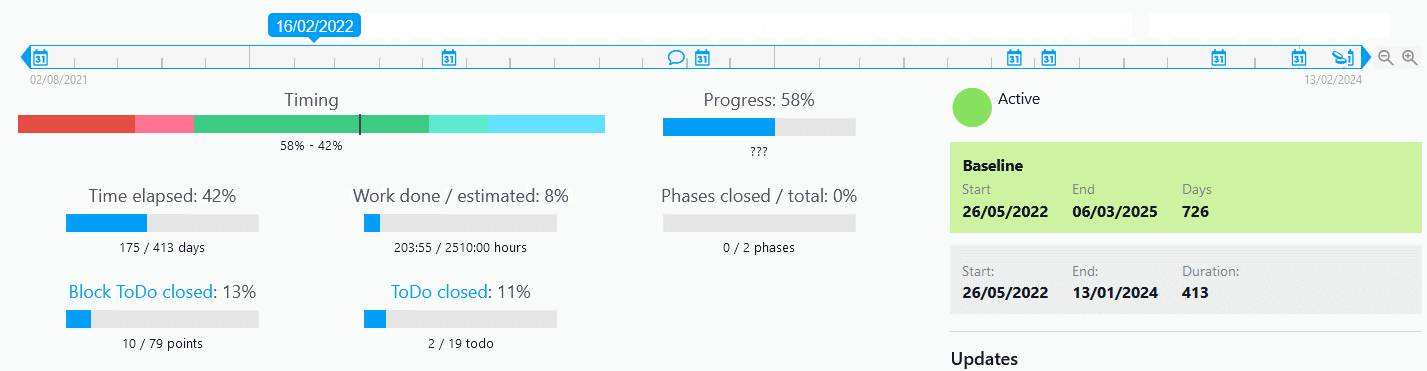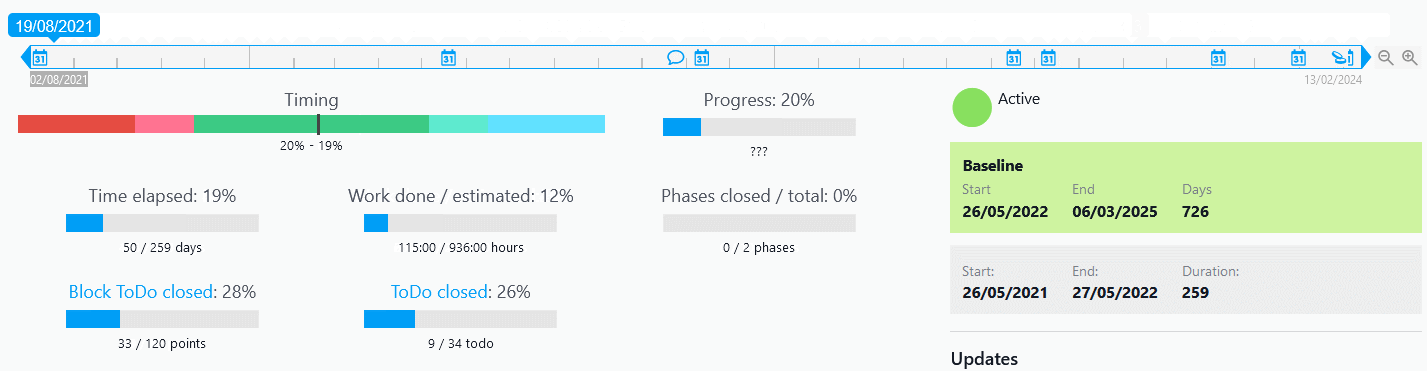
Twproject has a powerful and precise filter management applied to several functions of the platform. Even for Portfolio Management, filters help you select and display projects with an incredible variety of choices.
The filters can be combined with each other and refer to the three main areas of data, i.e. those relating to the project (type, budget, characteristics, etc.), the timeframe (duration, relevant dates, etc.) and the resources involved.
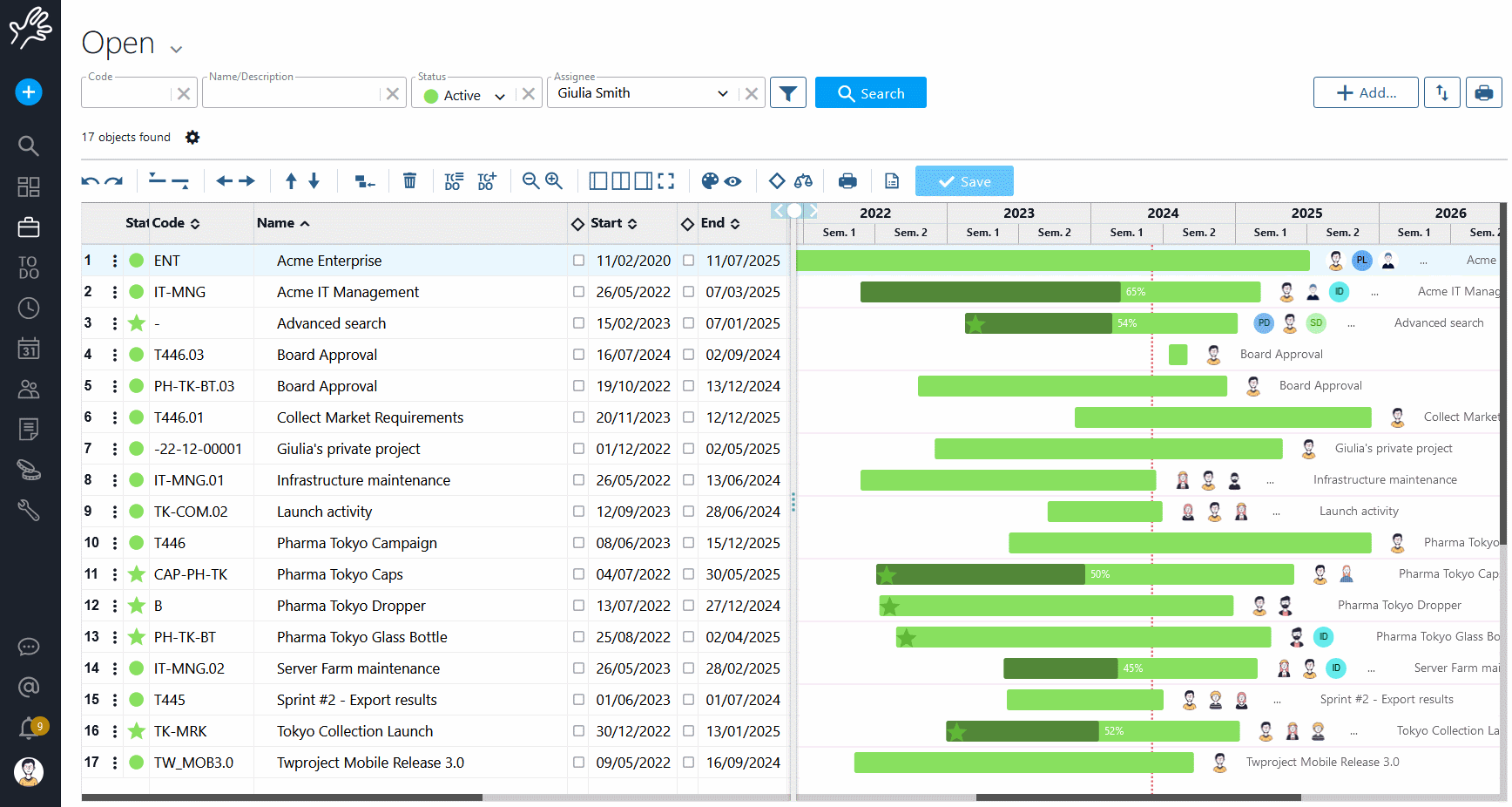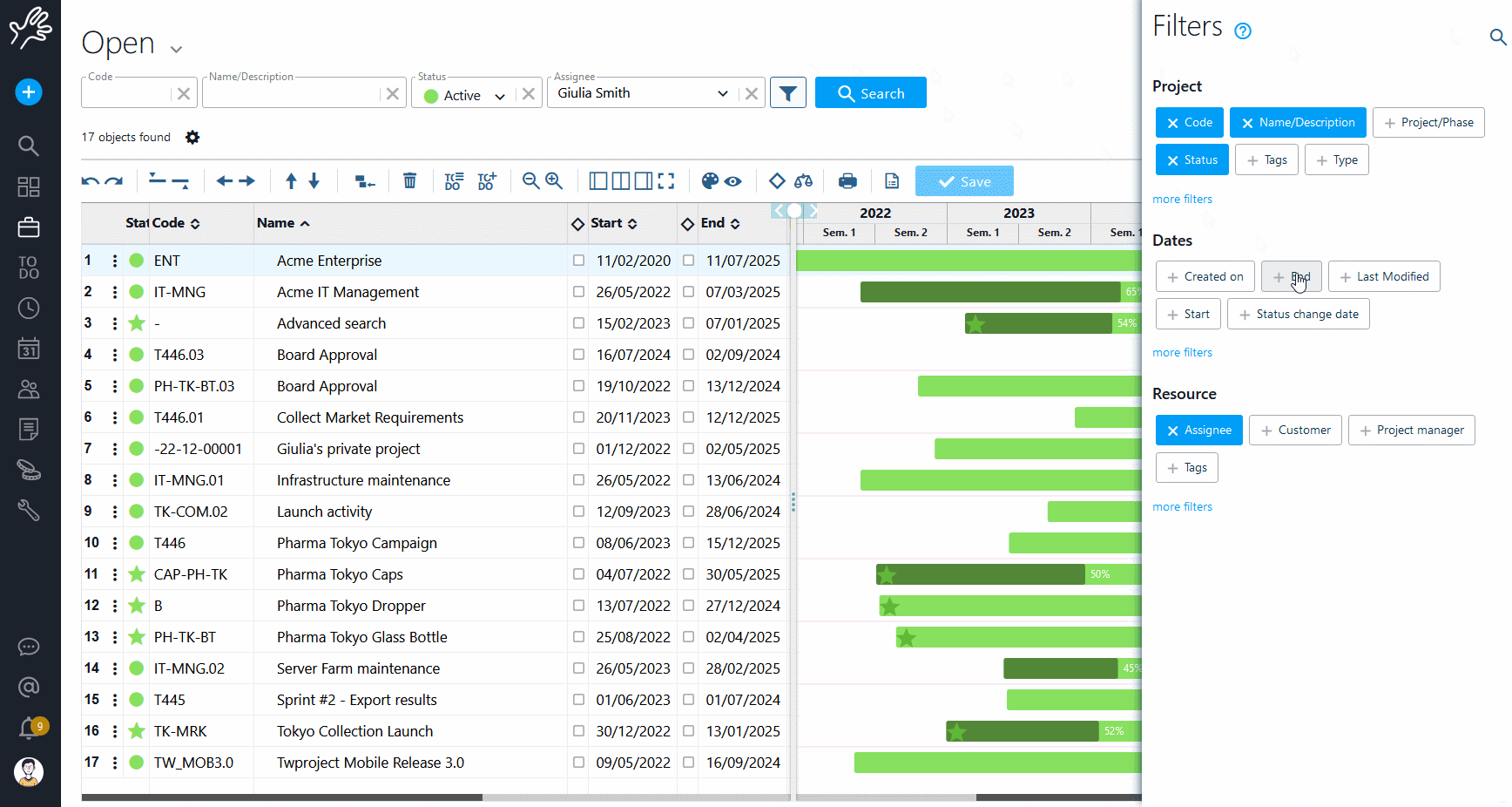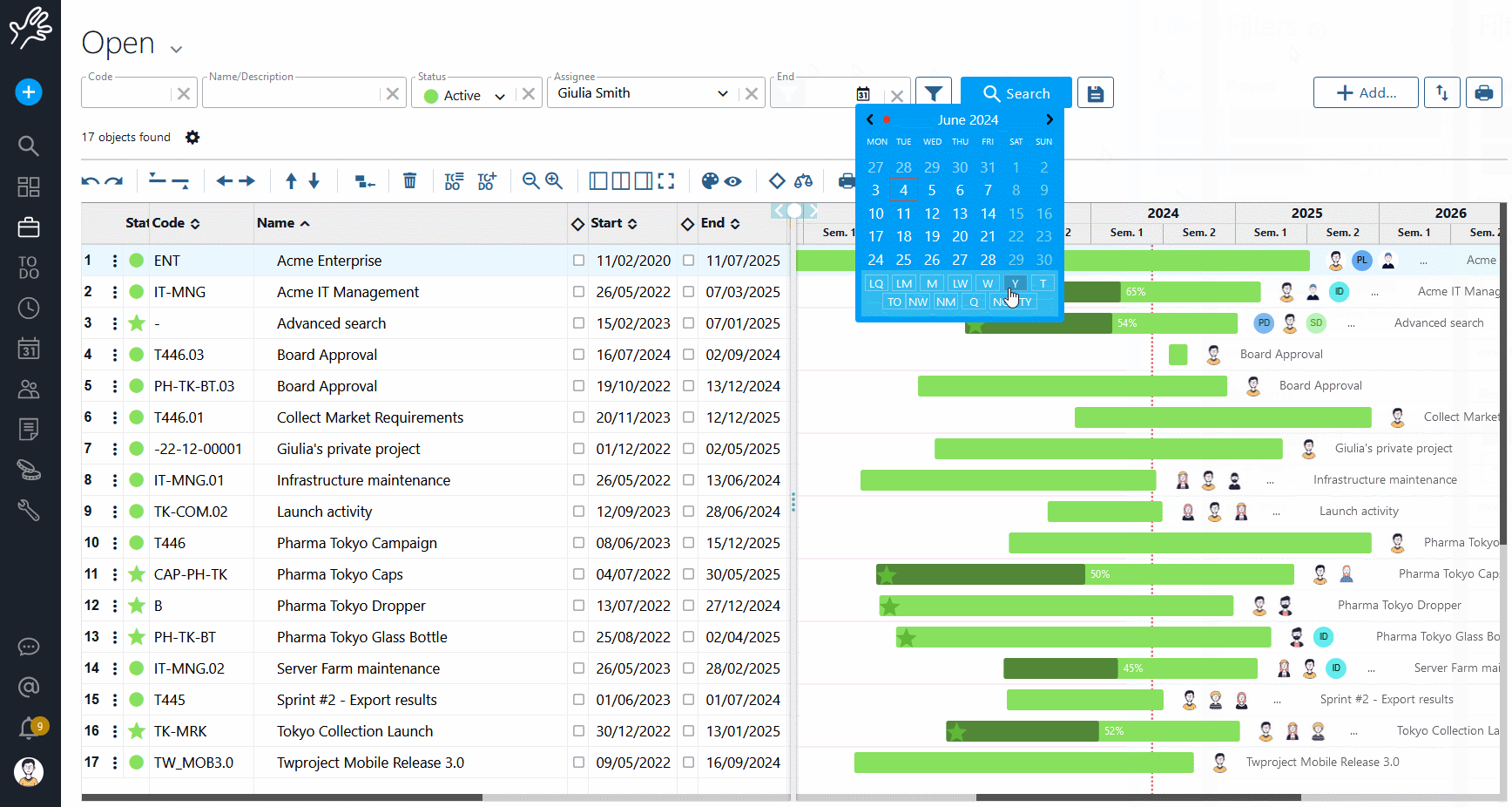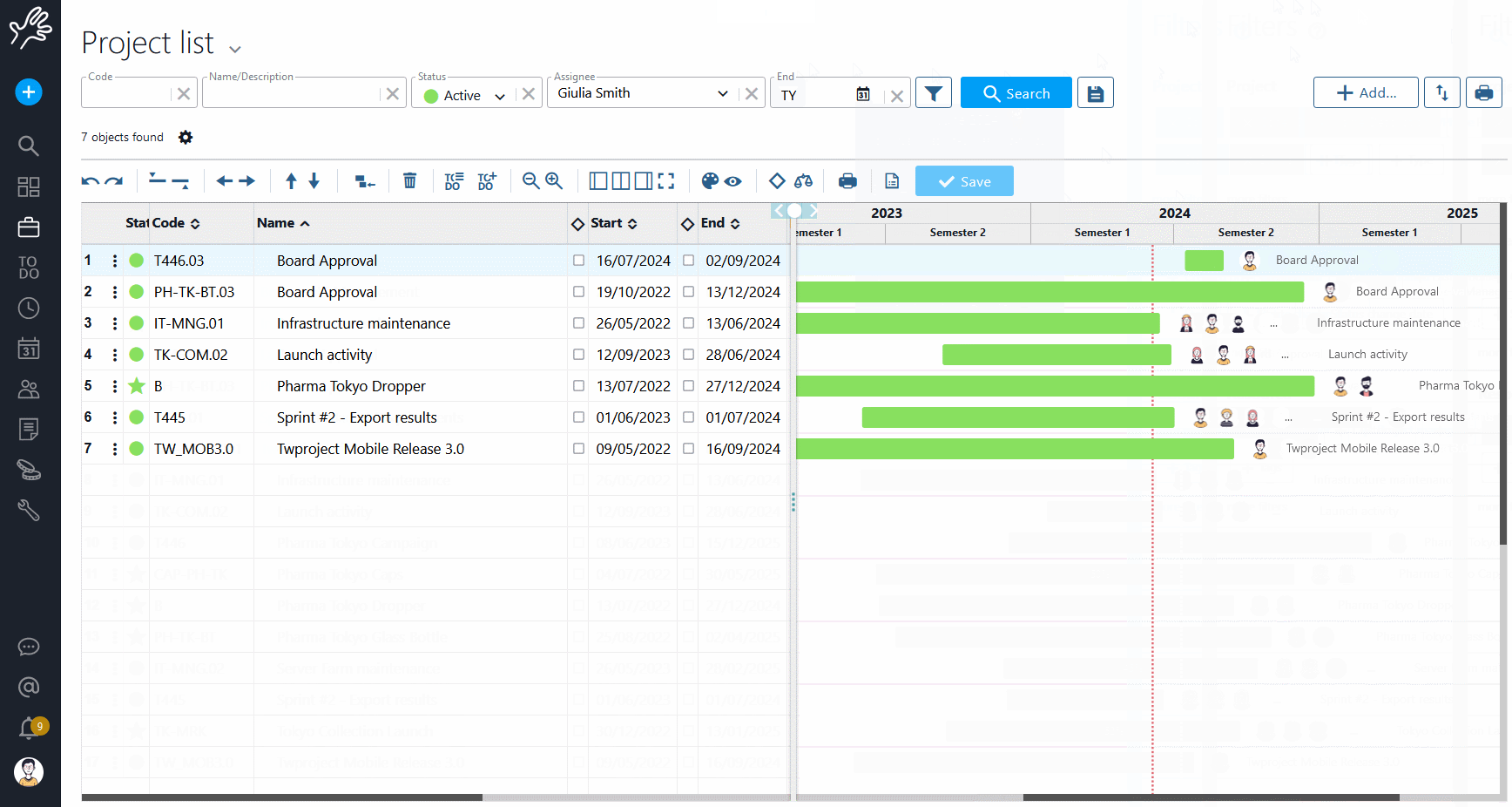
There is a default filter in the main search bar, but it is possible to save new customised configurations and even to define a specific filter as the default selection.
A good use of filters therefore meets the first requirement of Portfolio Management, namely to have an overview of specific areas or groups of projects.
In addition to the classic Portfolio view, it is also possible to filter in the statistics dashboard to get an overview of the performance of selected projects by different progress factors.
Financial management
In order to calculate the ROI and see which business objectives have been met, it is also important to keep an eye on the project budget when it comes to Portfolio Management.
Among the filters that Twproject provides, the ‘Budget overflow‘ filter is very useful, allowing you to select all projects that are experiencing financial difficulties.
This will allow us not to perpetuate the error and to take the necessary corrective action.
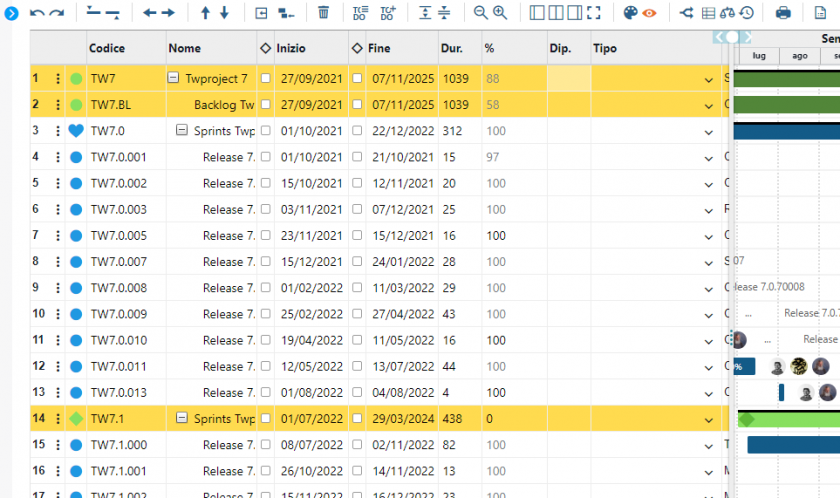
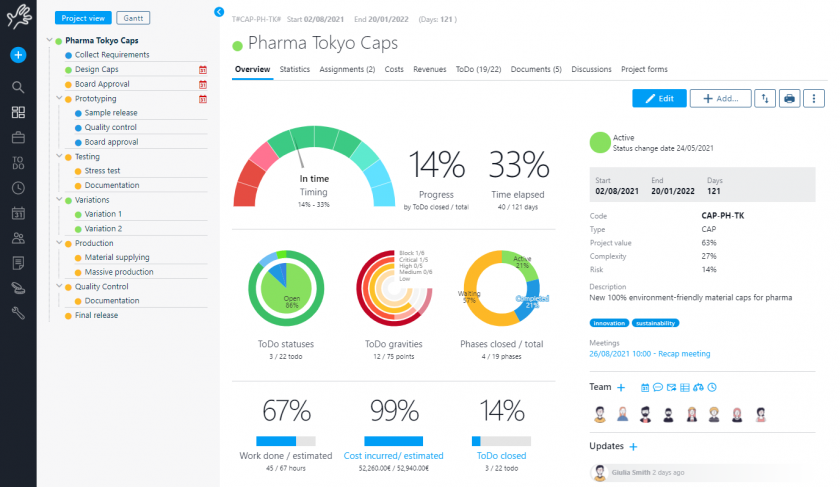
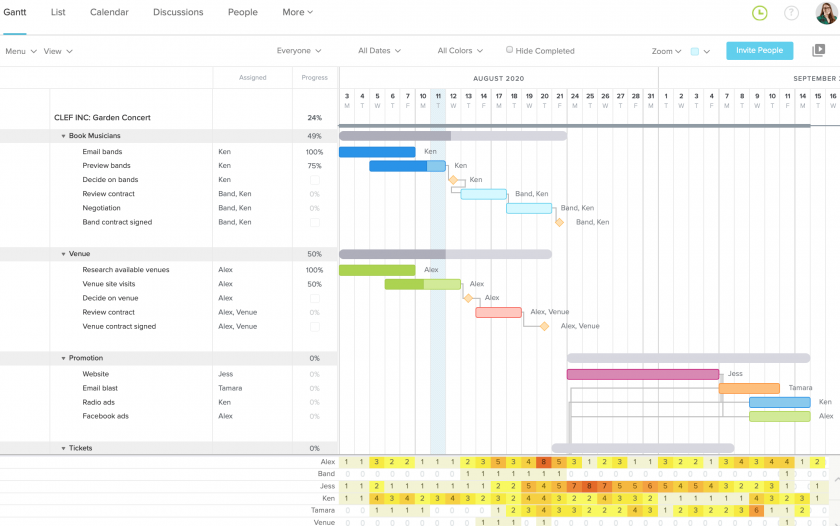
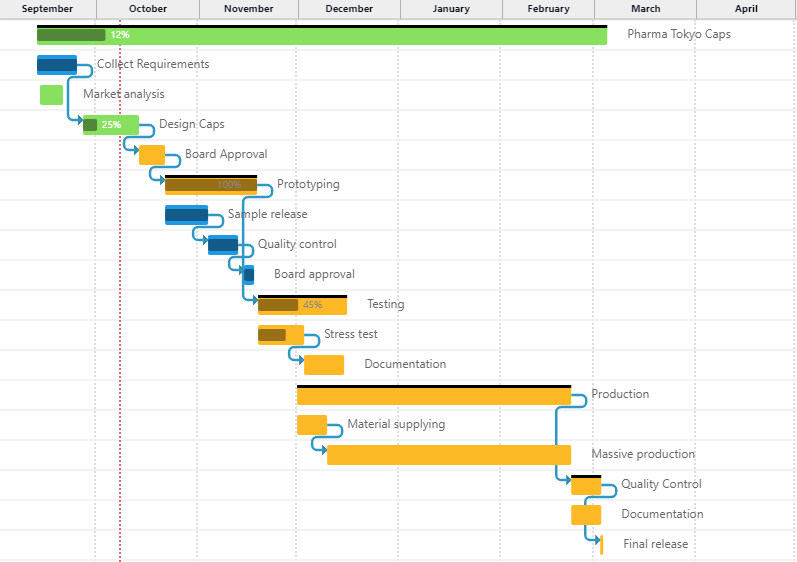
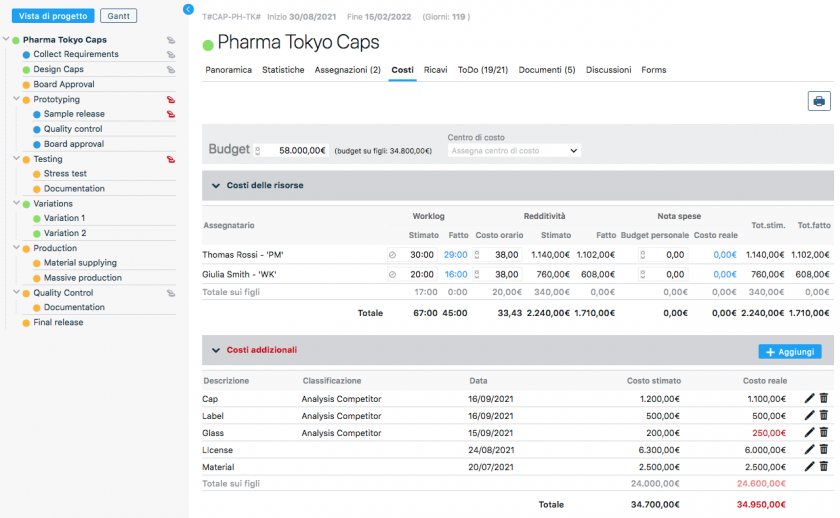
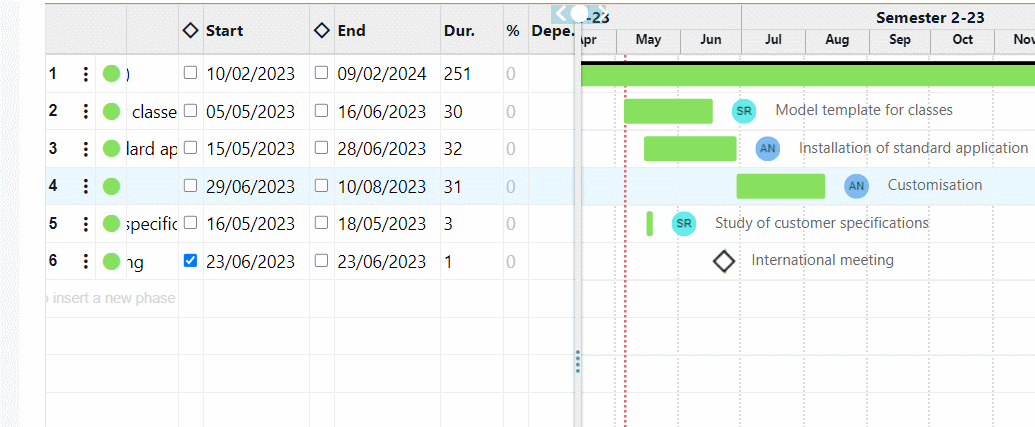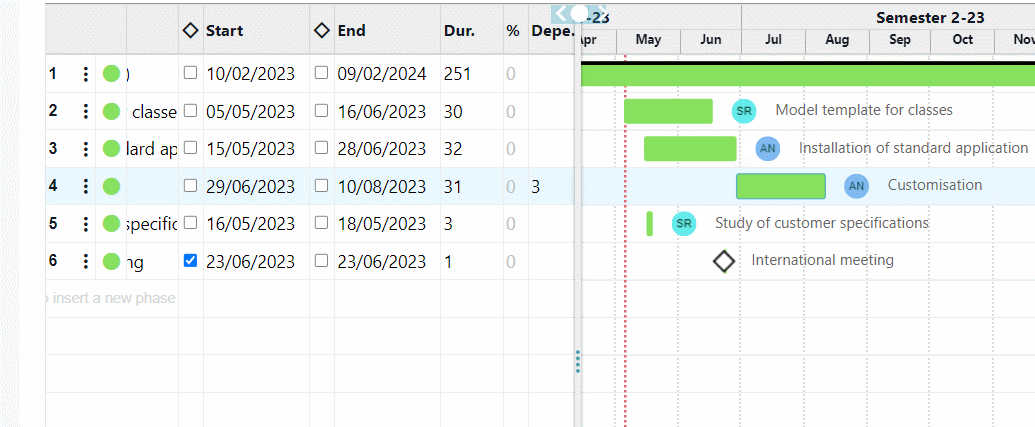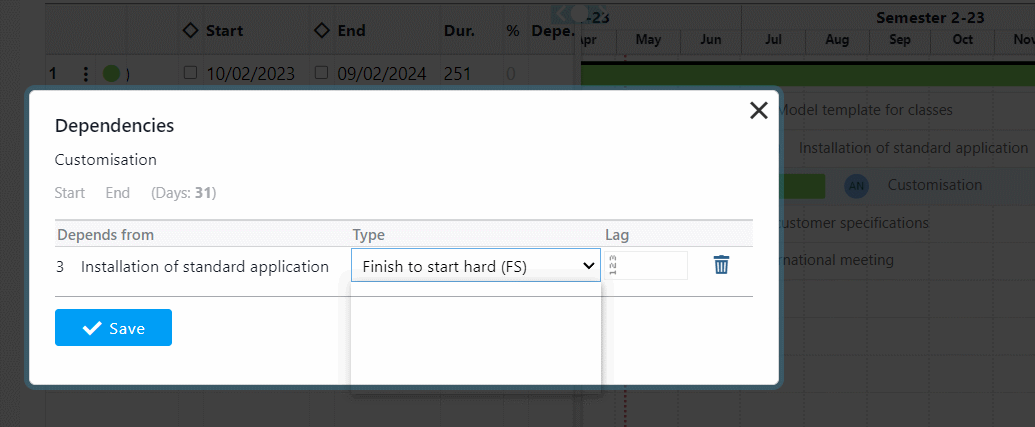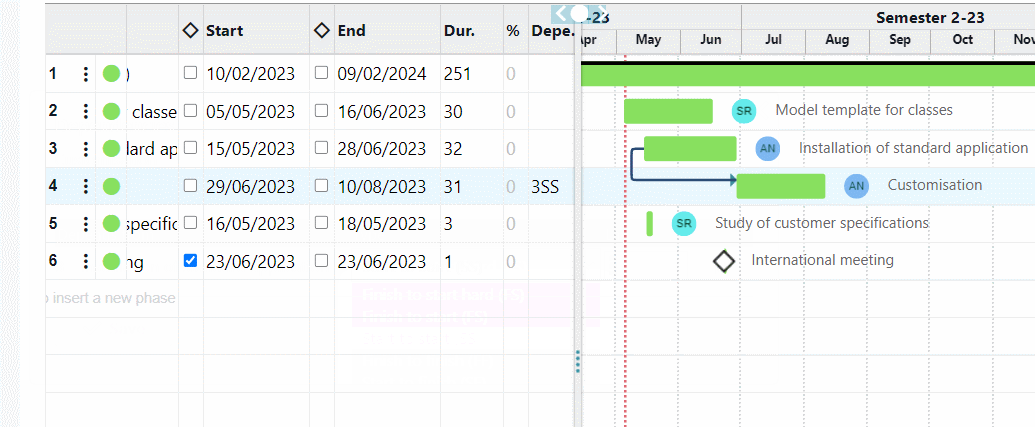
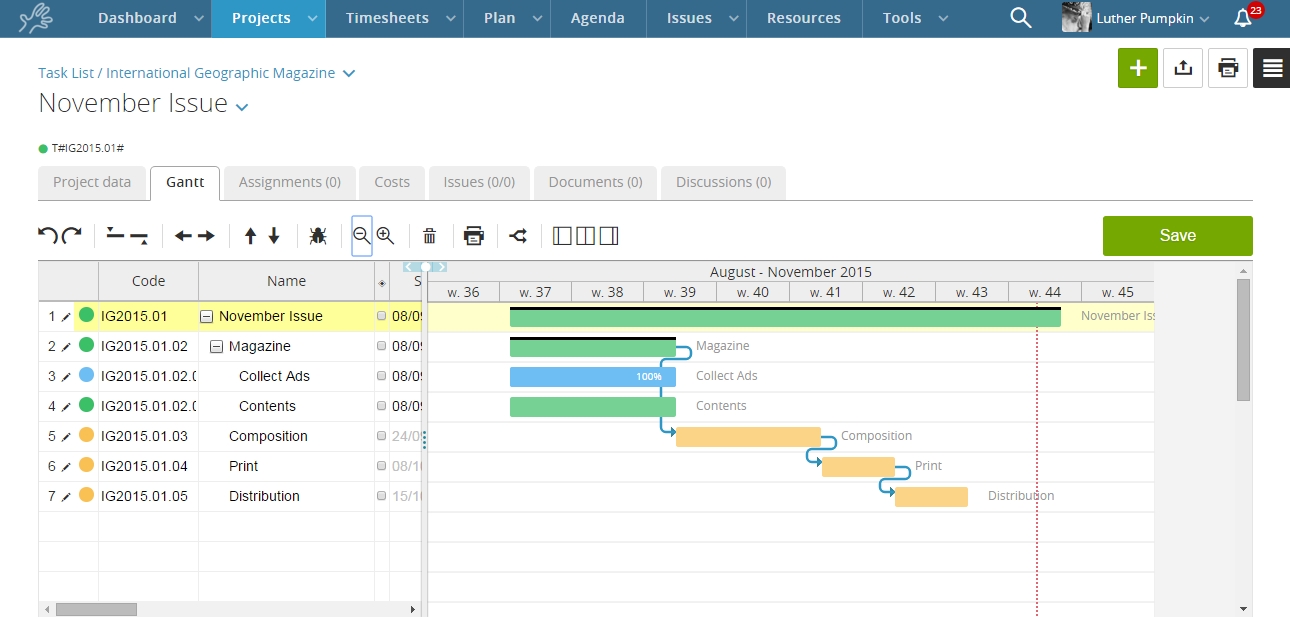
Furthermore, in the classic Portfolio view, which in Twproject is represented by a large global Gantt chart, we have the ‘Financial Data‘ command.
This function will allow each project in the list to be paired with its financial report, relating the budget with estimated and actual costs.
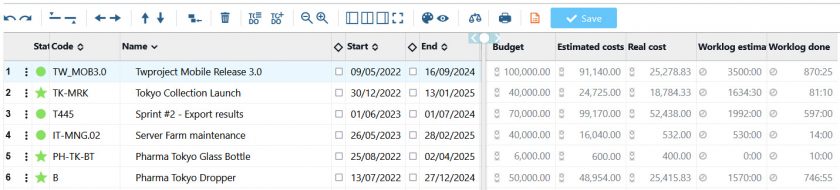
Such a view is very useful for carrying out cash flow analyses and evaluating the highest-performing projects at a glance.
In fact, financial management in Portfolio Management helps measure the value created by each project and make decisions on the most profitable investment areas.
Relevance among projects
After measuring the performance of projects, it is important that the digital tool allows the priority that each project has over the others to be set.
Twproject allows you to assign a relevance value to projects and this value can be defined and displayed in the Portfolio.
We can sort projects according to increasing or decreasing relevance so that timing and allocations can also be redefined according to this criterion.
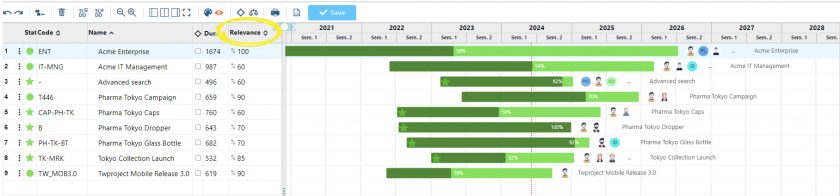
Indeed, through the Portfolio, you can easily reschedule the start and end dates of projects and relate them to the overall timeline.
For example, a less relevant project can be moved later in time, choosing to give priority to other, more beneficial projects.
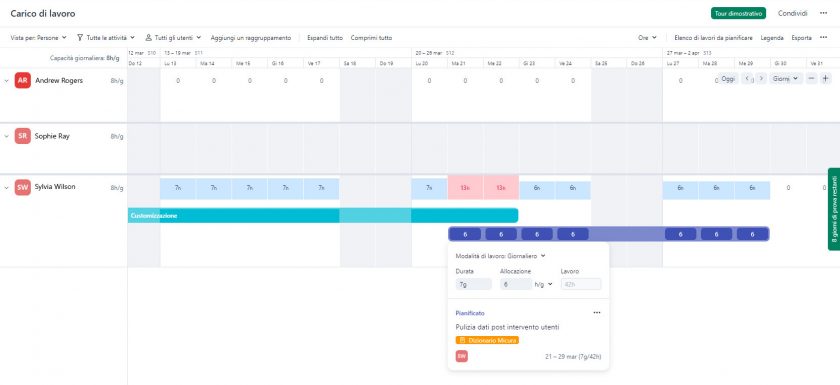
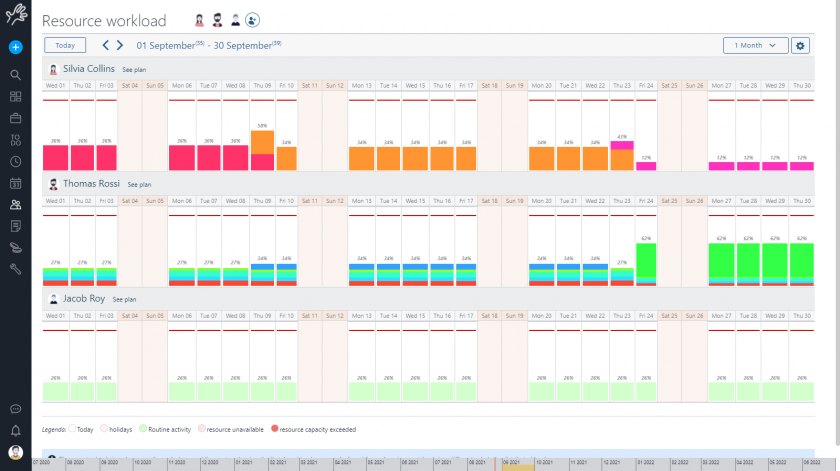
Resource management and allocation
Furthermore, an important function of Portfolio Management is the distribution of the workload between different projects, also according to their strategic and economic relevance.
Indeed, it is useful that the efforts of resources are well distributed, but also well focused on the projects that have the highest priority, both in terms of timing and strategic relevance.
This level of priority is only detectable, as we have seen, with the Portfolio Management activity.
Twproject takes this a step further and allows you to redistribute the load in an intelligent and thoughtful manner, with just one click.
Here is how you can do it with this simple trick:
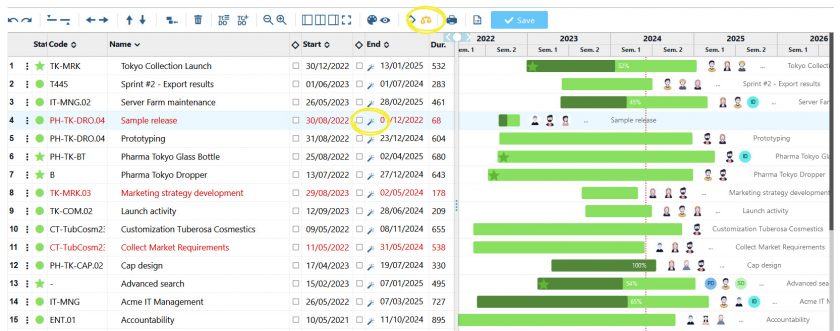
- From the main view of the Portfolio, see which of your resources are overloaded with the ‘show/hide workload’ icon (scale).
- Secondly, filter the projects by assignee, limiting the view to those in which the overloaded resource (or resources) is included.
- After filtering, arrange the obtained projects according to order of relevance.
- Finally, use the command ‘optimise end date by resource capacity’ (the magic wand) on the project with the lowest relevance: the dates of the latter will be extended until an optimal load for the person involved is reached.
Strategic planning that takes these factors into account increases corporate welfare and the satisfaction of the entire team.
As well as, of course, optimising overall productivity levels.
Shareability
Ultimately, the function of Portfolio Management is also to facilitate group communication and ensure that all parties involved in projects are coordinated with each other.
It is crucial to provide regular reports on the progress of the entire portfolio and its sustainability in relation to the company’s objectives.
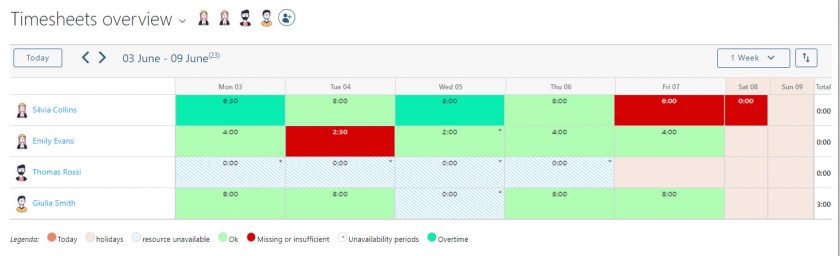
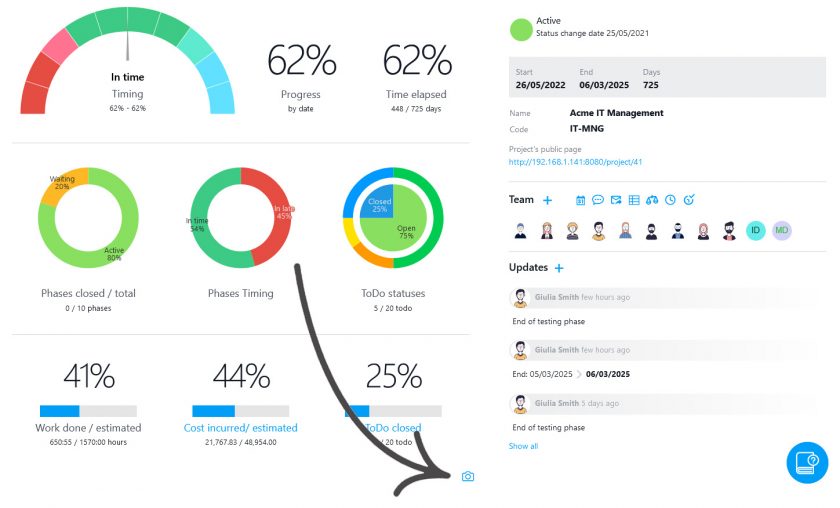
The Portfolio statistics dashboard in Twproject shows the overall status of the work, with graphs and insights updated in real time. We can filter this data for any need, as already seen, and easily export it in various formats for full sharing.
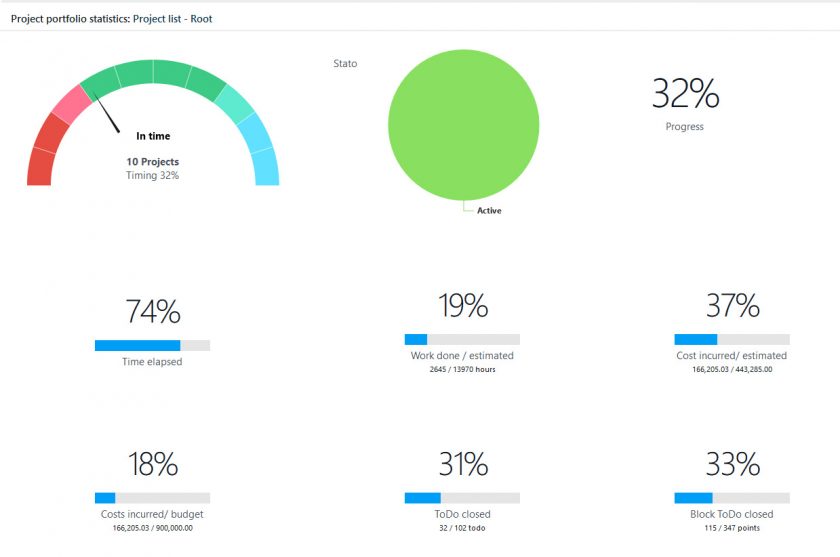
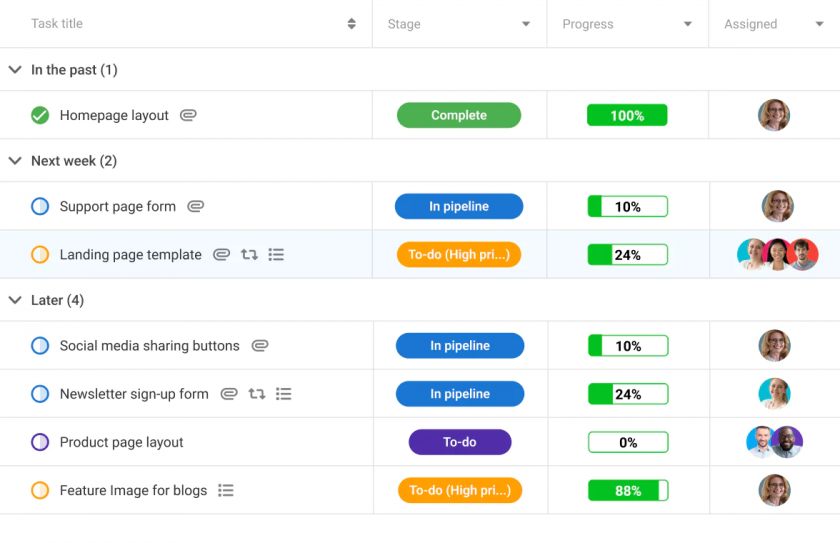
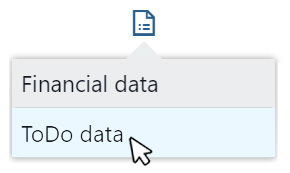
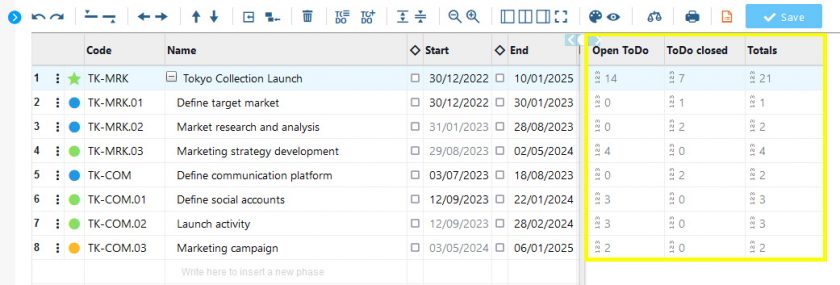
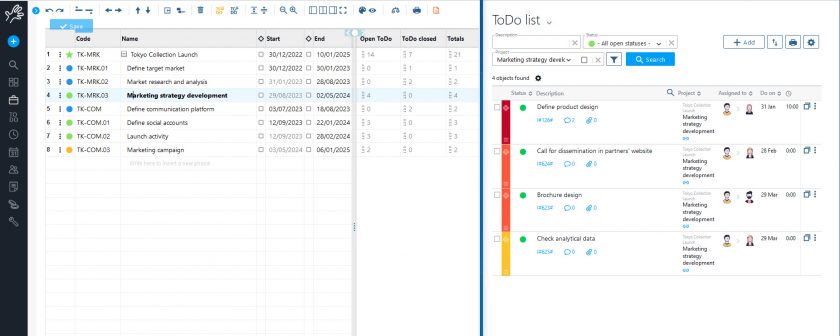
In addition, on the main page of Portfolio, you can put information on the status of ToDos next to each project line, thanks to the ‘ToDo Data’ command.
Knowing the status of activities for each project is very useful for planning purposes, but also for sharing the up-to-date situation with the resources involved, in a cohesive effort to achieve objectives.
Indeed, creating a collaborative environment for a faster exchange of information is one of the objectives of Portfolio Management, with the ultimate goal of smoothing the planning of activities and their monitoring.
Twproject answers the central question of Portfolio Management
We can summarise all the operations we have seen with a single question that the Portfolio Manager tries to answer with the most suitable tools.
The question is: which projects contribute to the corporate strategy and should therefore be given higher priority, and which should be eliminated or postponed?
Twproject is a unique tool that answers this question, and it does so in an articulate manner, providing you with concrete data for your analyses.
Each analysis objective is covered with Twproject: the total cost of each project, the consumption of resources (human and other), the planned duration and investment schedule, the benefits and the relationships or interdependencies with other projects in the portfolio.
You do not need anything else for the overall planning of your business projects and Twproject guides you step by step.
If you want to put it to the test, you can make a free 15-day subscription during which you will see how to perform all the main Portfolio Management activities, with the help of our support team.
Put us to the test!