-
Expense report: how to manage it in complex projects
Expense report management is one of companies’ most sensitive and tricky tasks, especially for large projects. The expense report is a core document that accounts for costs incurred by an employee during a trip or as part of a specific project. Managing it can be challenging due to the variety of expenses involved and the … Continue reading "Expense report: how to manage it in complex projects"
-
How to use the cost center to simplify large projects
The cost center is a valuable tool for simplifying the financial management of projects. Accurate and detailed cost management is critical to ensure sustainability and growth in any company. Elements such as raw material, unit cost, and other economic factors are essential to the success of any business. But how can all these elements be … Continue reading "How to use the cost center to simplify large projects"
-
7 project management books to read on vacation
Are you looking for project management books to read on vacation? You are in the right place! Summer is a great time to relax, replenish your energy, and read. If you are passionate about project management or wish to improve your skills in this domain, there is no better time to dive into inspiring books. … Continue reading "7 project management books to read on vacation"
-
Team performance domain: what’s new PMBoK 7
Team Performance Domain is one of the 8 Project Performance Domains introduced in PMBOK’s seventh edition. These replaced the 10 Knowledge Areas featured in the previous Project Management Body of Knowledge edition. This article will explore what this is all about and what this change implies for project management. CONTENT INDEX Project Performance Domain: what … Continue reading "Team performance domain: what’s new PMBoK 7"
-
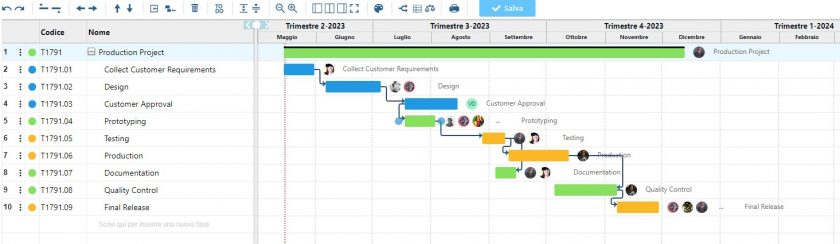
New Twproject Release 7.1.004 – All types of Gantt dependencies
After months of study and implementation we are really happy to announce that a new version of Twproject has been released and it includes, among other optimizations, a particular step forward on the use of the Gantt chart. The Gantt developed by Twproject is undoubtedly one of the best on the current market in terms … Continue reading "New Twproject Release 7.1.004 – All types of Gantt dependencies"
-
Women quota in project management: what are the challenges in 2023?
Women share in Project Management is a topic we hold close to our hearts. Our company is committed to gender equality, having a fair proportion of men and women. The project manager role is one of the most important and fast-growing occupations worldwide, and women are becoming increasingly present in this field. CONTENT Statistics on … Continue reading "Women quota in project management: what are the challenges in 2023?"
-
PMBoK 7 vs. PMBoK 6: Evolutions, Challenges, and Jokes for the Modern Project Manager
CONTENT PMBoK 7 vs. PMBoK 6: introduction to the differences 1.Basic principles 2.Performance Domains 3.Hybrid and agile approaches Project Manager Challenges in Consideration of PMBoK 7 1.Adapting to a more flexible and agile approach 2.Managing stakeholder expectations 3.Focusing on value creation 4.Managing uncertainty and risk 5.Developing personal skills and leadership 5 practical tips for tackling … Continue reading "PMBoK 7 vs. PMBoK 6: Evolutions, Challenges, and Jokes for the Modern Project Manager"
-
7 tips to boost work productivity
CONTENT 7 tips to increase work productivity 1. Focus on one activity at a timet 2. Take regular breaks 3. Focus on the most important tasks first 4. Set small goals 5. Delegate some tasks 6. Boost work productivity: use the tomato technique 7. No meetings Boosting your team’s work productivity is no impossible feat, … Continue reading "7 tips to boost work productivity"
-
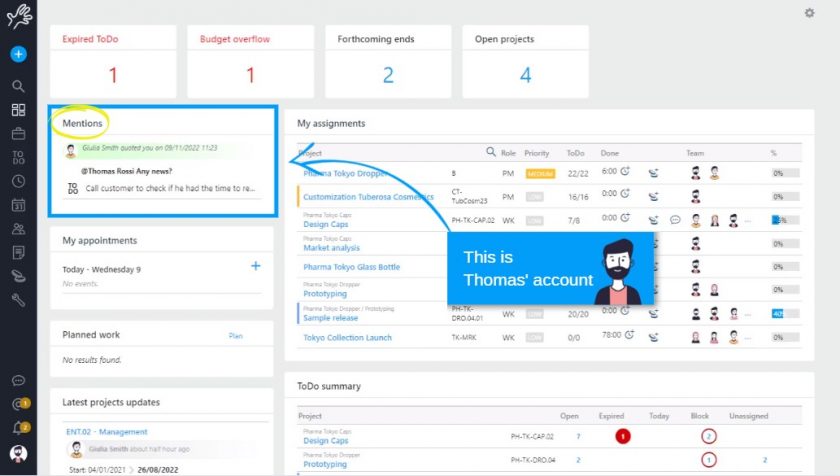
Twproject 7.1.000 – Introduction of mentions and other improvements
Communication is an essential requirement within a team; that’s why in Twproject you can find many different features having this goal. Today we added an brand new one: the mentions! Twproject 7.1.000 includes also several security fixes and improvements. Mentions are now available in Twproject Nowadays, using constantly messaging applications, we got used to mentions, … Continue reading "Twproject 7.1.000 – Introduction of mentions and other improvements"
-
How important time management is for better productivity
Good time management skills can help in every area of people’s lives. CONTENT What is time management? Benefits of time management 1. Less stress 2. Better work-life balance 3. Improved concentration 4. Less procrastination 5. Increased energy levels 6. Improved work quality 7. More opportunities 8. Better work image 7 tips for successful time management … Continue reading "How important time management is for better productivity"
-
Make or buy? How important the Project Manager is in decision making
“Make or buy” is one of the strategic choices that project managers face in project management. CONTENT Make or buy: 6 factors of decision making 1. Existing skills 2. Potential skills 3. Revision time 4. Cost evaluation 5. Quality comparison 6. Emotional reasons Make or buy analysis: project manager’s role Make or buy: strategic and … Continue reading "Make or buy? How important the Project Manager is in decision making"
-
Time reporting: clarity and straightforwardness thanks to a software
Time reporting is a critical component of project management. CONTENT Why use time reporting software? How does software time reporting work? 1. Addition of time entries 2. Time tracking 3. Reporting Choosing the right tool Time tracking provides a way to track the hours spent on individual activities and the overall project. The best way … Continue reading "Time reporting: clarity and straightforwardness thanks to a software"
-
Project variance: how best to manage it
Project variances are a real nuisance, and successful project managers must manage them as best they can. CONTENT What are design variations? Why is change management important? How to best manage the project variance 1. Initiating a change request 2. Evaluation of the change request 3. Analysis of the change request 4. Implementation of the … Continue reading "Project variance: how best to manage it"
-
Sprint planning: how to plan it to achieve your goals
Sprint planning is an essential part of the Scrum management process. CONTENT What is sprint planning? Sprint planning execution 1. Sprint planning meeting 2. Past sprints review 3. Establishing your sprint goal 4. Break down the objective into tasks Resource allocation 6. Setting a time period 7. Measuring progress 8. Sprint review Benefits of successful … Continue reading "Sprint planning: how to plan it to achieve your goals"
-
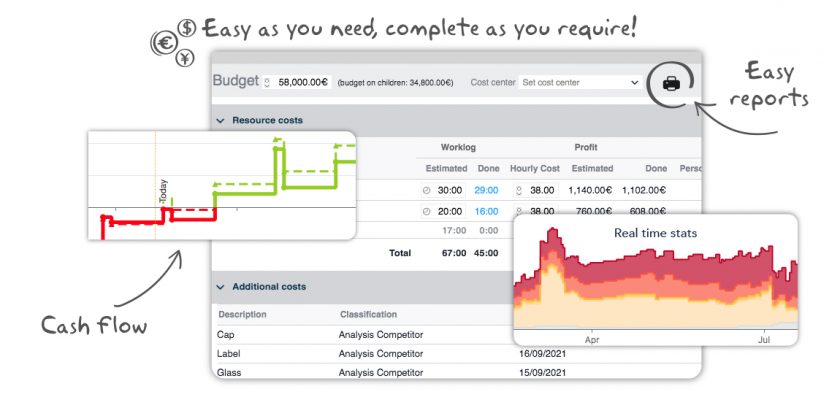
Project costs: everything under control
A successful project must not only be on time, but also on your budget. In this article we will see how Twproject manages project costs. The overall cost of a project depends mainly on the scope of application; the list of items contributing to the total will be very different between a consultancy project, a … Continue reading "Project costs: everything under control"
News
Choose the category you are interested in:
AgileComparisonCost managementPm expertProduct updatesProductivityProject managementResource managementTime managementUsage tips