The WBS examples in this article will help you understand how to break down a project in a clear and structured way.
To ensure the success of a project, project managers need to know how to break down the project and, consequently, how to structure a WBS to ensure the success of a project.
WBS is the abbreviation of Work Breakdown Structure, which, in other words, means a division of the labor required to complete a project.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
The WBS is widely used by professional project managers to represent the scope of the project and the results in a hierarchical manner.
Generally, creating a work breakdown structure is one of the first steps in project planning.
For project managers at the beginning of their careers, sometimes the WBS can be confusing and difficult to manage, but it is good that they quickly become familiar with it, because it is the key to success, especially in the case of complex projects.
The Work Breakdown Structure, in fact, is used to make complex projects more manageable. In essence, the WBS is designed to help divide a project into manageable blocks that can be effectively assessed and controlled.
How to break down a project: why do you use a WBS?
Obviously, a simple list of the activities and the people who will follow the project is not enough to clearly divide the project into smaller pieces.
Therefore, the use of a work breakdown structure provides a clear view of the project’s scope of work.
In a work program, the activities are grouped under certain levels of decomposition.
For example, in a construction project program, the electrical wiring activities are grouped in the level dedicated to the electrical system, while the piping activities are grouped in the level dedicated to mechanical works.
Therefore, the WBS allows to improve the quality of planning, traceability, and reporting and this is why it is used.
It should be kept in mind though, that the WBS describes the final results and the activity groups, not the activities in detail.
In short, some widely used reasons for creating a WBS include:
- Help with an accurate project organization
- Help to assign responsibilities
- Show project control points and milestones
- Allow a more accurate estimate of costs, risks, and time
- Help explain the scope of the project to stakeholders
How to break down a project correctly
To start, the project manager and the experts determine the main final results for the project.
Once determined, it is possible to begin to break down these results into smaller and smaller work blocks.
But how small? This depends on the type of project and the management style, but some sort of rule should be established in order to determine the size and scope of the smallest work blocks.
For example, the two-week rule could be chosen, in which no piece / activity is smaller than two weeks of work required for completion.
Or, another method is the 8/80 rule, where no block should take less than 8 hours or more than 80 hours to complete.
Determining these rules for block sizes can take some practice, but these make WBS definitely easier to use and structure.
Regarding the format chosen for the WBS design, some project managers prefer to create tables or lists, but most use graphics to visualize the components of the project, such as a hierarchical tree structure or a diagram.
At Twproject we use the project editor, which allows us to create the WBS in a few clicks. The WBS is fully integrated with all project information, it shows you the status of the phases and any critical issues as well.
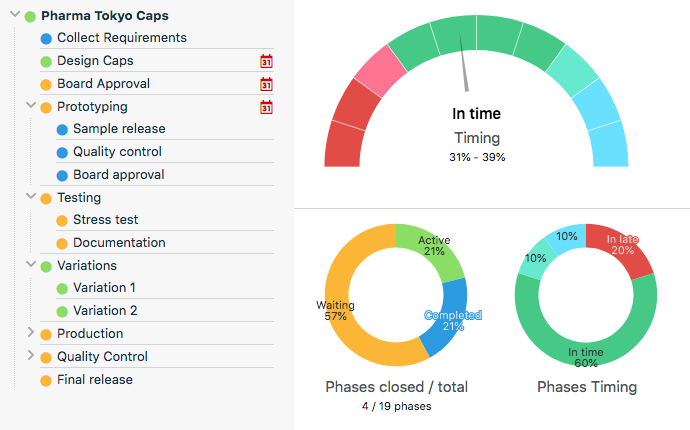

Create your WBS in few clicks
In Twproject, creating the project WBS is very simple thanks to an inline editor that allows you to have the structure available in a few clicks, one step away from the Gantt..
Create your WBS with TwprojectHow to simplify a project: some examples of WBS
The WBS diagram starts with a single box or another graphic element, usually positioned at the top, which represents the entire project.
The project is then divided into main components with related activities or items listed below them.
In general, the superior components are the final results, while the lower level elements are the activities that lead to creating the final results.
Here are some simple examples of WBS:
Developing a computer:
Suppose your organization intends to start developing a computer.
To speed up the work, you can assign specific teams to different aspects of computer construction, as shown in the diagram below.
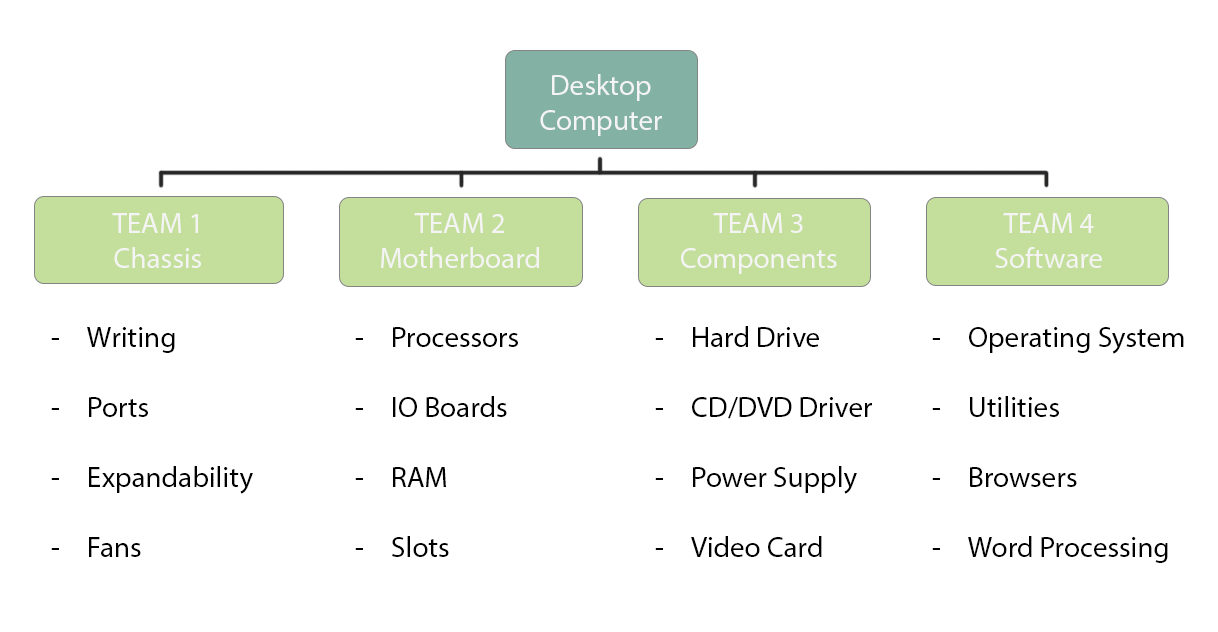
In this way, a team could work on the configuration of the frame, while another team will be dedicated to protecting the components.
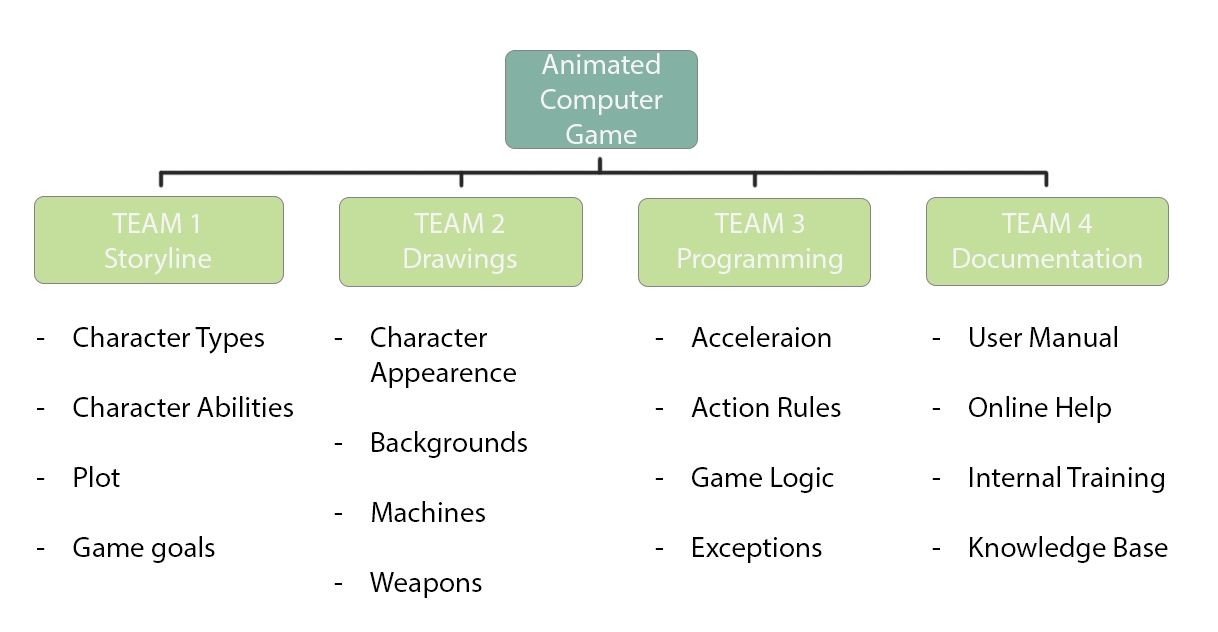
Developing a computer game:
Let us now think, for example, that your organization wants to manage a project dedicated to a software, specifically the creation of a computer game.
To be the first to launch the game in the market, it is necessary to assign specific aspects of the game to different teams, as shown in the diagram below.
In this case too, each team will need to focus on its own work package to efficiently complete each phase of the project.
Construction project:
The convenient format of a Work Breakdown Structure allows you to use it for any type of project and, therefore, it is also useful in the case of a construction project.
This example of a work breakdown structure shows that all the elements are listed in the various levels of the WBS.
The lower levels of the structure show the results of the project. Tasks and activities will be grouped under these lower levels.
Level 1 is the overall project. Level 2 represents the main phases of the project. Level 3 shows the main final results, while level 4 represents the minor results.
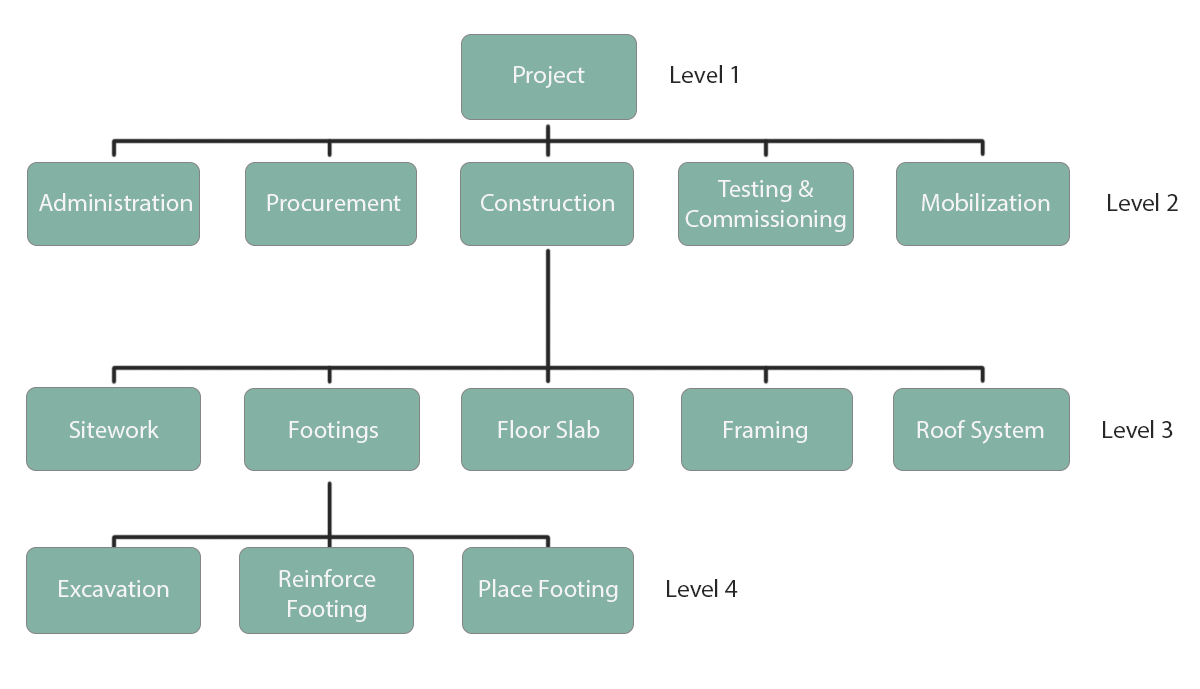
The construction of an effective project work sharing structure can, in the long term, determine the success of the project.
See how to set up your projects with Twproject starting from the definition of the WBS and some examples
As you can see, the WBS is the foundation of project planning, and allows you to better manage cost estimation, scheduling and resource allocation, not to mention risk management.
As we have seen with the previous examples of WBS, this one will be one of the first documents to be created in the project management lifecycle. In fact, the work breakdown structure already arises from the project plan and defines the hierarchy of the final results.
Finally, the WBS provides a visual presentation of the project, graphically organizing the results. In Twproject this overview is particularly relevant: you will be able to have a unified view of the fundamental structure of the project, i.e. all that is needed for its completion.
Twproject has allowed us to organize work subdivision in a simple way through the WBS, then planning the duration of the phases and the workload of each assignee by using the Gantt chart.

5 errors to avoid when creating your WBS
Even a well-thought-out WBS can fail if you make strategic mistakes in its construction. Here are the most common ones:
- Going into too much detail
Over-subdivision creates confusion and slows down management. Keep it useful, not obsessive. - Skipping the 8/80 rule
Each work package should take between 8 and 80 hours to complete. Too small or too large = unmanageable. - Confusing activities with deliverables
The WBS shows what needs to be delivered, not how. Activities go in the project plan, not in the WBS. - Not assigning responsibility
Each package must have a contact person. No responsibility = no execution. - Making a WBS “just for the sake of it”
Using it only as a static document means you lose its potential. Integrate it into your tools (such as Gantt charts, effort tracking, costs).
Twproject is a tool that can support you in the creation of all the key elements of project planning, starting from the WBS, and that will follow you throughout the project, helping you with many indispensable tools for your business.
Try it for free and let us know about your experience. For any questions, you can contact our support team.




