The quality plan is often overlooked in project development, yet it is strategic in defining the route and results, let’s see how.
CONTENT
- What information should a project plan include?
- What is project quality planning?
- Project quality plan model development
All projects, at their end, must produce / provide something, the so-called project output.
In the start-up phase, the client and the project manager, along with the project team, jointly set the project goals and timelines for completion.
The project deliveries must therefore meet certain general industry quality standards as well as customer-specific requirements.
Therefore, all project outputs – whether they are one or many – must be validated and verified prior to delivery to the client.
Quality should be considered not only in the output, but also in the processes and activities that produce these results.
Generally speaking, if the processes and activities that produce the deliverables do not meet quality standards, it is very likely that the output will not meet the delivery quality standards.
Thus, the quality plan becomes an essential document for the project.
This plan acts as a “quality bible” for the project and all stakeholders should agree to it.
The project’s quality management plan will determine the relevant quality requirements and standards that project deliverables must meet and will define a plan on how to meet them.
In short, it means providing a defect-free product developed with the highest efficiency.
What information should a project plan include?
In order for the plan to be complete, there are a series of information that should not be overlooked. We have drawn up the following list of data to be included in a quality management plan:
- Describe project objectives and quality expectations in general.
- Determine the organization’s quality policies and management systems (e.g., ISO 9001 certification) and outline how these policies will apply to the project.
- Identify other quality criteria or policies that must be adhered to and complied with, such as customer or investor requirements.
- Describe how quality requirements will extend throughout the supply chain.
- Define acceptability criteria for project deliverables.
- Define quality management roles and responsibilities.
- Identify which standards will be applied.
- Identify and list the quality metrics that need to be monitored.
- Describe monitoring and reporting processes to provide constant improvement.
- Describe design and review processes.
- Describe testing and quality assurance processes.
- Describe the processes for dealing with defects.
- Describe project acceptance processes.

What is project quality planning?
Project quality planning can be a challenging process, but it allows an organization to clearly set quality requirements and document all necessary procedures for managing expectations in this regard.
The development of a quality plan model is thus a key activity. Without a complete project quality plan it is almost impossible to implement the project and deliver the product on time, within budget and according to stakeholders’ requirements.
Project quality planning is one of the key elements of strategic project management; it is the starting point to create a link between stakeholder expectations and product requirements.
There are several inputs involved in running the project quality planning process. These are:
- Scope statement,
- Stakeholder requirements,
- A list of identified and described risks (the so-called “risk register”)
- Project implementation program.
By using all this input information, the project manager, supported by their team, should develop a model project quality plan.
Project quality plan model development
Although each project is unique, a standard approach can still be used for the development of a quality plan model.
Here are the key steps:
1) Collect input data
As already mentioned, in order to develop a model project quality plan, it is necessary to collect input information, including the scope statement, stakeholder requirements, risk register and the project implementation program. The project manager and the team must ask for all the necessary information and collect the requirements for the product.
2) Set quality parameters
Here you must decide which metrics and parameters will be applied to analyze data and activities throughout the project lifecycle.
Some of the most common metrics include:
- Accuracy of deliverables: Measures compliance with technical specifications.
- Timing of deliverables: Assesses adherence to schedule.
- Customer satisfaction: Can be measured through feedback and surveys.
- Defect rate: Number of errors or problems detected in deliverables.
3) Analyze data
As soon as the input information is collected, the next step is to perform a cost-benefit analysis. This analysis will help to review all the costs that will be involved in the project and all the benefits stated during the project setup phase.
Through Twproject‘s reporting tools, cost-benefit analysis becomes more intuitive, facilitating informed decisions based on up-to-date data.
Quality planning activities are aimed at meeting quality requirements within the planned costs and reported benefits. Simply put, the cost of each activity should be compared with the expected benefit and, according to the quality parameters chosen, the ratio should be at least satisfactory.
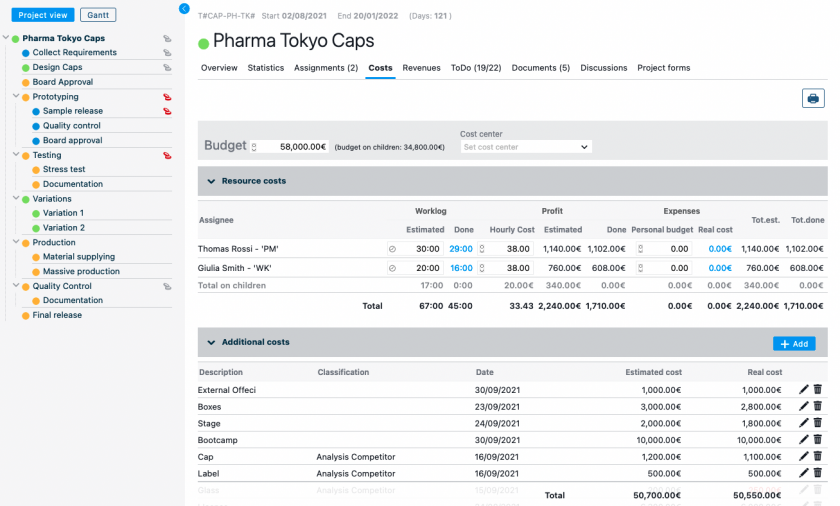
4) Perform quality control
Throughout the project lifecycle, quality metrics will have to be observed and it will be essential to establish how to control these characteristics during the project implementation process. You can use checklists and templates to guarantee consistency in quality metrics and to take control of the expected quality performance.
5) Progettazione del piano di miglioramento
The ultimate step in developing a model project quality plan is to create an improvement plan that outlines the actions to analyze quality performance and identify activities to improve the value of the project / product.
This quality plan may include steps and reasons to apply changes to the project, product setup or process metrics.
With Twproject, you can quickly identify areas for improvement and implement corrective actions efficiently.
To sum up, a quality plan is a fundamental document in a project to ensure its success.
It is about creating a foundation for setting requirements and identifying quality procedures.
Just as in a project you have defined objectives and results, so the quality metrics must also be well set.
Quality plans provide an essential framework for ensuring that every aspect of the project meets the expected standards. These plans help to identify areas that can be improved and ensure that the project can undergo rigorous quality assessments.




