Tangible and intangible benefits are crucial to launch any project.
Usually, the tangible benefits are mostly considered when evaluating a project, but there can also be several intangible benefits.
CONTENT
- What’s the difference between tangible and intangible benefits?
- Tangible benefits
- Revenue increase
- Resource cost savings
- Increased productivity
- Tangible benefits
- Process improvement
- Intangible benefits
- Organizational strategy support
- Enhanced user experience
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Greater compliance
- Brand equity
What’s the difference between tangible and intangible benefits?
Tangible benefits are those that can be measured in financial terms, while intangible benefits cannot be quantified directly in economic terms, but still have a very significant business impact.
The intangible benefits, sometimes also called “soft benefits”, are the profits ascribable to the improvement project that cannot be reported for formal accounting purposes.
These benefits are not included in financial calculations because they are not monetary or are difficult to quantify and calculate.
Material benefits are physical in nature and may represent long-term or short-term benefits, while intangible benefits usually represent long-term assets that are not physical property but rather the intellectual property of an organization.
Another difference between these two benefits is that intangible benefits can increase or decrease over time, while the tangible benefits of a process are unlikely to fluctuate.
And, again, tangible benefits can often be estimated before certain actions are taken, while intangible benefits are virtually impossible to estimate beforehand.
Here we will see specifically what the tangible and intangible benefits of a project can be.
Tangible benefits of a project
Revenue increase
Questo è il tipo di vantaggio più comune di un progetto, ed il più auspicato dagli stakeholders.
L’aumento delle entrate è un vantaggio quando un progetto ha un impatto diretto sulle entrate dell’organizzazione.
A queste entrate possono aggiungersi altre fonti di entrata aggiuntive quali il lancio di un nuovo prodotto o la fornitura di un’offerta.
L’aumento delle entrate è rappresentato da un valore in denaro preciso.
Resource cost savings
Sometimes, adjustments to the system or the renovation of work processes aim to make the cycle of a project with its phases more efficient.
In these cases, it may therefore happen that a certain activity is not necessary after the implementation of the changes. This benefit can also be achieved when any system or process problems are resolved. In this case, it may happen that the organization may make some roles redundant or assign some resources to a different department, which means an optimization or decrease in resources and, therefore, their costs.
Increased productivity
A tangible project benefit is increased productivity (also read 7 tips to boost work productivity) that may allow people to work more or be rerouted to other areas.
Sometimes, system or process problems force people to perform a manual solution, repeat tasks more than once to correct or lead more people to revise the same task.
Using a tool such as Twproject, it is possible to monitor and optimise each project phase, reducing time wastage and increasing operational efficiency.
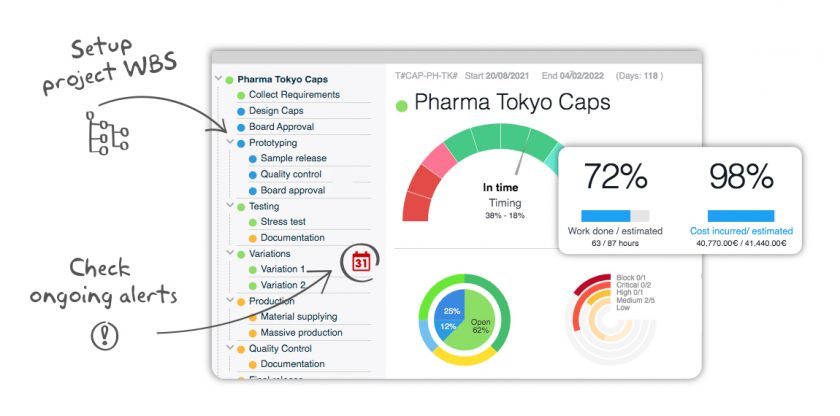
Process improvements
Processes can improve the time required to complete a given project. It can be a matter of automating a simple manual data entry operation or a complex process that would require a lot of energy, time and cost. Improving processes means that the time needed to complete a process is shorter, which can save time by freeing up the resource for other tasks.
Intangible benefits of a project
Organizational strategy support
Among the intangible benefits we find an increased market position and/or the perception by customers that the organization is an industry leader.
Organisational and intellectual capital play a key role in creating and sustaining these perceptions, turning into a lasting competitive benefit.
Enhanced user experience
Some projects may create a product that is easier for final customers to use or provides innovative features.
This results in a significantly improved user experience (UX), representing an intangible advantage to all intents and purposes.
Improving UX means creating products that are more intuitive, easy to use and enjoyable for the end user.
For example, if a project focuses on creating a more intuitive user interface (UI) for software, users can complete their tasks more quickly and with less frustration. This not only increases productivity, but can also lead to greater customer satisfaction, an intangible but crucial benefit.
Increased customer satisfaction
The projects in general aim to provide satisfaction to the final customer, whether this is external or internal to the organization. Otherwise, if the client is not satisfied with the result, the project could not be considered successful. However, increased customer satisfaction is an intangible benefit since it is not possible to measure it objectively.
Greater compliance
Some projects intend to rework systems or processes that will undergo an audit process. If an organization violates a regulation or a compliance policy, it could end up facing huge fines. Sometimes a project benefit is just this: doing something to provide greater organization security.
Brand equity
Brand equity is one of the key goals for most organizations. Some projects seek to improve brand equity by providing better services and keeping standards. This is another example of an intangible benefit.
Sometimes, tangible benefits are considered more important than intangible ones. This because they are quantifiable and immediately recognizable.
However, it is necessary to remember that intangible benefits deserve the same consideration, since they constitute a significant part of an organization’s value.
According to economists, more than 25% of the value of companies is now based on intangible assets, such as brand image and market share.
Here is how it becomes essential, during a project analysis, to consider tangible as well as intangible benefits and to consider them equally important.
Human resources and human capital
Human resources play a key role in the success of any project. Human capital, i.e. the skills, knowledge and experience of employees, is an intangible resource that can significantly influence the results of a project.
Investing in a new resource through training and development can increase the organisation’s intellectual capital, thus contributing to competitive advantage.
Tangible and intangible benefits: choose the right tool
A software such as Twproject can help you monitor benefits. You can start very easily by setting up the parameters that will allow you to monitor increases in tangible fields, such as productivity and cost savings.
In fact, Twproject has a very intuitive and customizable user interface that allows you to track every single aspect of your project’s progress, including operational processes.
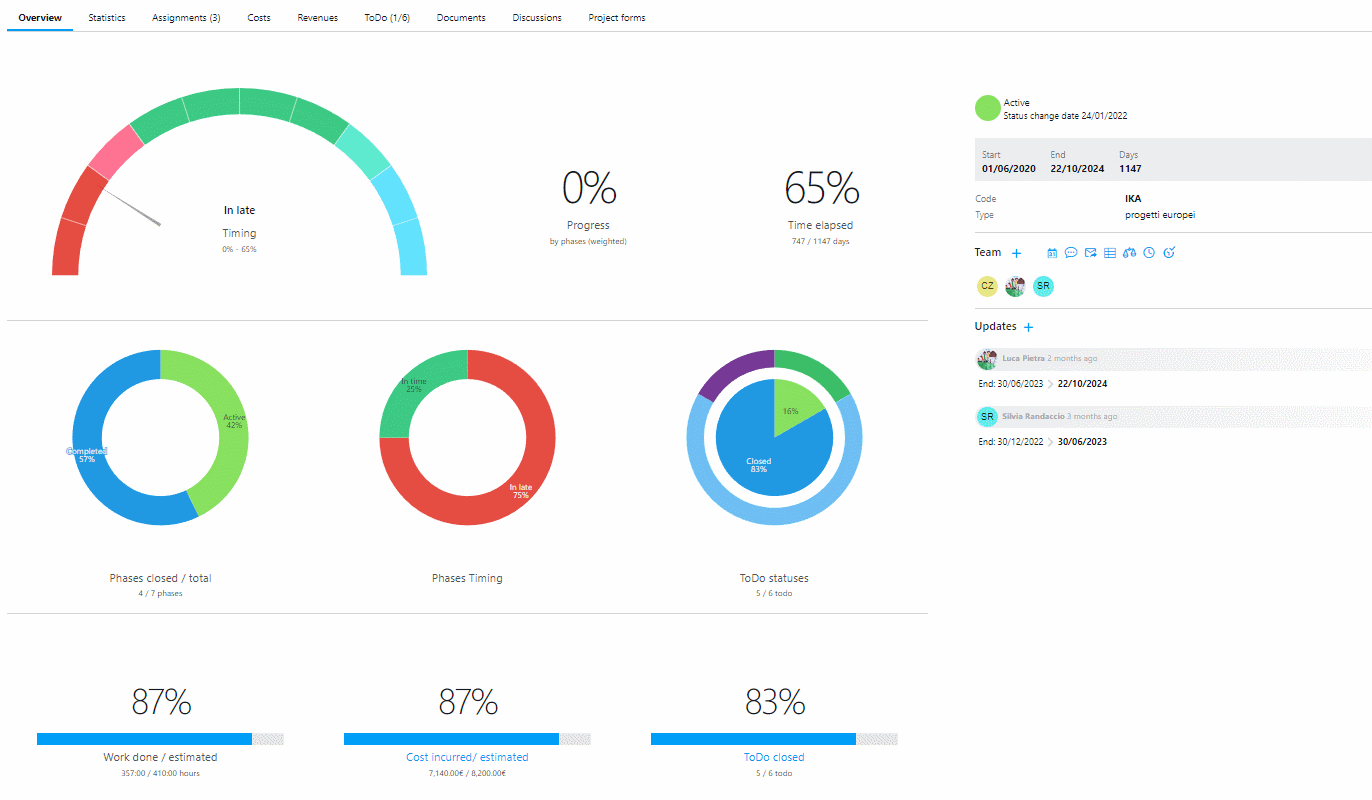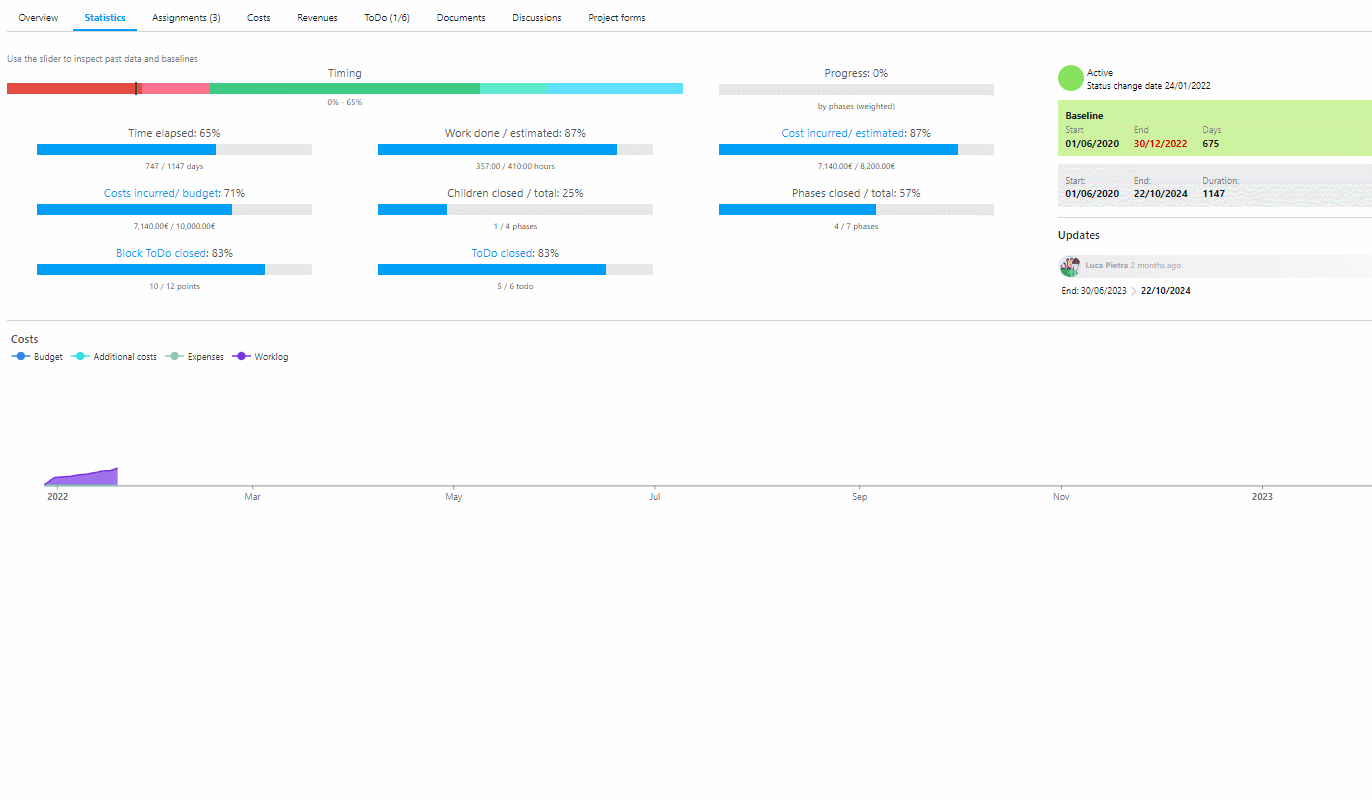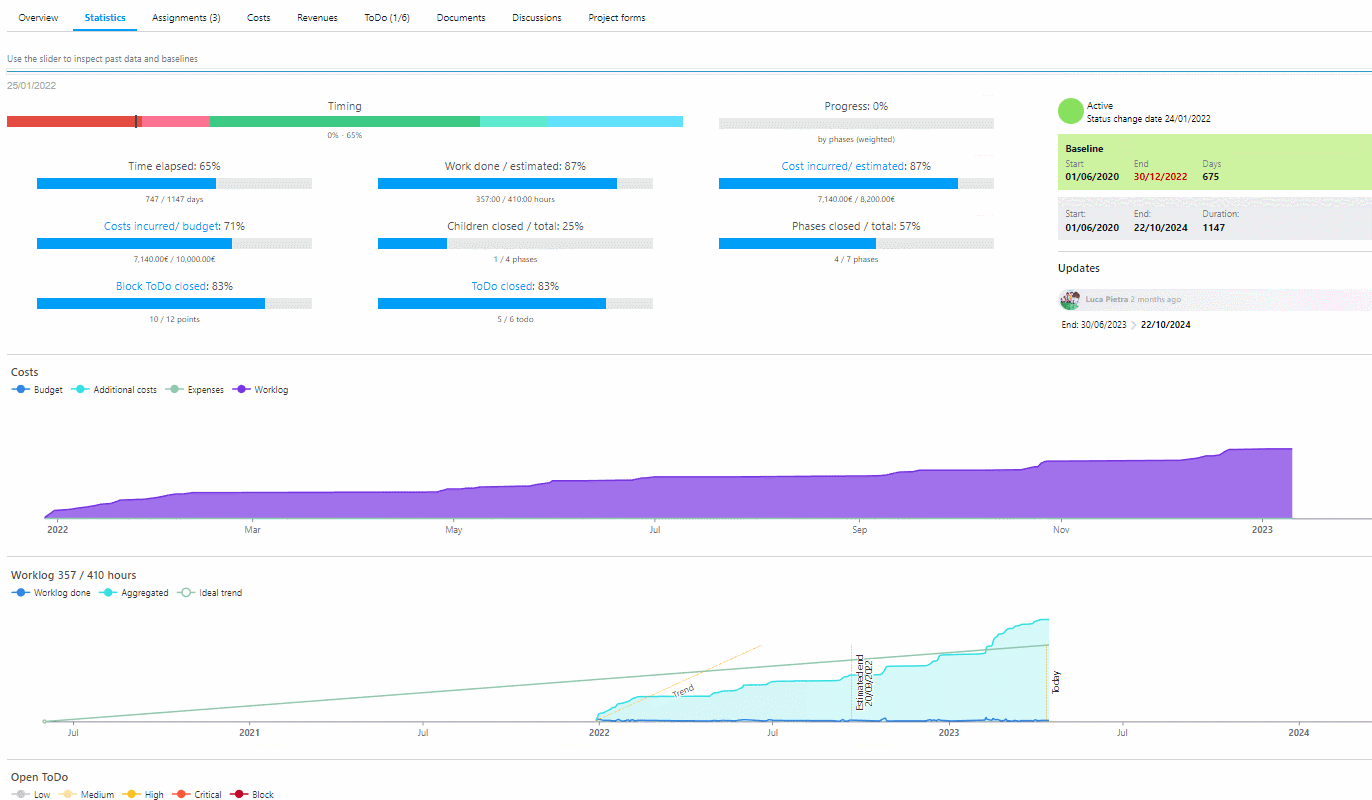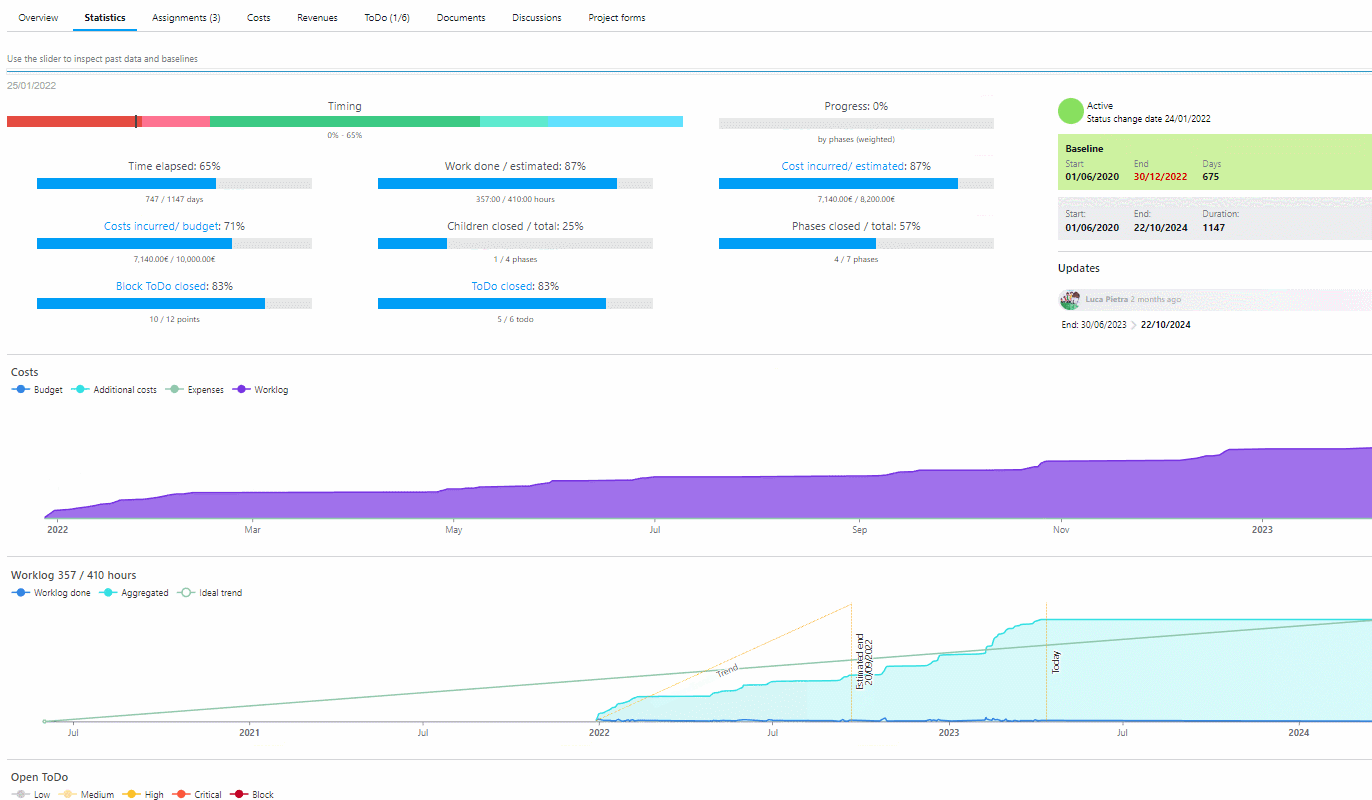
Over time, you’ll learn to use this tool to monitor intangible benefits as well, since this software offers great versatility and its reports are highly adaptable to your needs.
The data collected through Twproject’s monitoring tools can eventually be aggregated and constitute the final value of the project.
In fact, among the customised forms offered by the platform, you will find one specifically dedicated to determining ‘Project Value’. The fields entered are customisable and include tangible and intangible benefits.
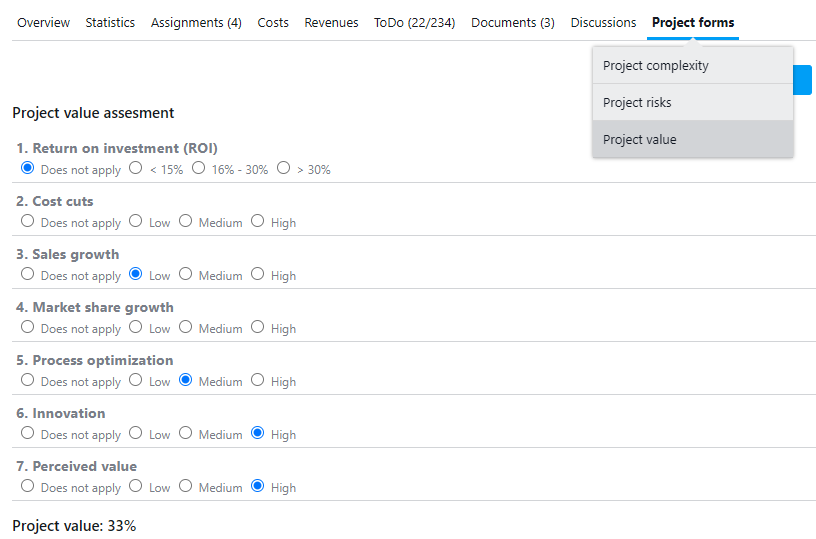
By scoring the various fields, you will be able to obtain an overall project value, which will help you benchmark your current projects.
If these features can be useful to you, you have the chance to take a free 15-day trial during which our team will be by your side to help you set the parameters that work best for you.
Don’t miss this opportunity and join us!




