Qualitative evaluation is one of the most strategic steps in project management. Unlike purely numerical analyses, it helps understand perceptions, experiences, expectations, and risks that are “invisible” in Excel spreadsheets.
For a project manager, knowing how to perform it correctly means reading beneath the surface and gaining a more complete view of the project, integrating measurable information with deeper interpretations.
In this article, we will look at what it is, how it is structured, and which qualitative research methods to use, including a comparison between qualitative and quantitative methods, which is now essential in modern project management.
CONTENT
- What is a qualitative project assessment?
- Qualitative and quantitative assessment: two complementary approaches
- What methods to use for qualitative evaluation
- 1. Structured and semi-structured interviews
- 2. Focus groups
- 3. Direct observation
- 4. Document analysis
- 5. Concept maps and journey maps
- How to perform a qualitative assessment correctly: the operational guide
- When qualitative assessment really makes a difference
- Why integrate tools such as Twproject into qualitative assessment
What is a qualitative project assessment?
Qualitative assessment analyzes the non-numerical elements of the project: stakeholder opinions, perceived risks, team collaboration level, operational criticalities, customer satisfaction, and cultural or communication barriers.
It focuses on the perspectives of the people involved, because these are precisely what can be decisive in determining whether a project is proceeding in the right direction or needs corrective action.
Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numbers and indicators, qualitative assessment interprets context, emotions, reactions, and motivations.
Qualitative and quantitative assessment: two complementary approaches
A professional project manager must know how to combine qualitative and quantitative approaches at every stage of the project.
- Quantitative assessment answers the question “how much”: budget, time, performance, and KPIs.
- Qualitative research answers “why”: motivations, resistance, perceptions, and sense of priority.
These two components are inseparable. Even the most robust quantitative research is incomplete if it does not understand people’s behavior. This is where qualitative research methods come into play, which are essential for understanding the real-world context in which a project operates.
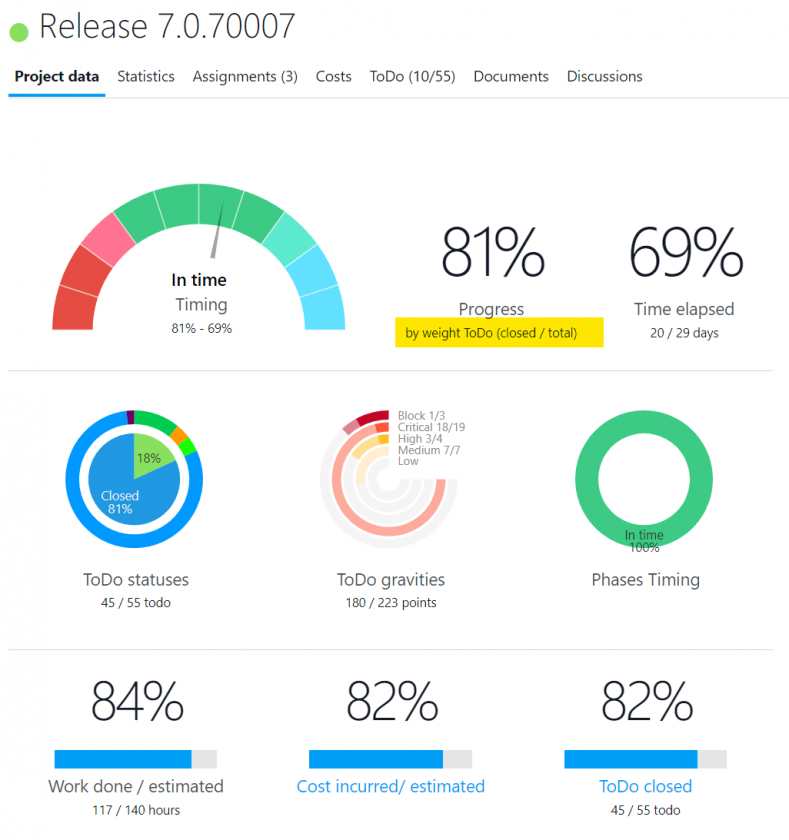
Twproject, for example, allows you to monitor indicators and progress, as well as collect feedback, conversations, and contextual notes, thus combining numerical analysis and qualitative input in a single platform.
What methods to use for qualitative evaluation
1. Structured and semi-structured interviews
Interviews allow you to gather detailed information directly from stakeholders, customers, or team members. They allow you to explore everyone’s points of view and bring out issues that have not yet been explicitly stated.
They are ideal when the project manager needs reasoned answers or wants to understand internal dynamics that can help optimize collaboration.
2. Focus groups
Focus groups are one of the most widely used techniques in complex projects. They bring together several people simultaneously, allowing you to observe interactions, agreements, and conflicts.
It is instrumental in market research to understand how a product or service is perceived by potential users, and in project management to understand team motivation, priorities, and critical issues.
3. Direct observation
The project manager analyzes behaviors, work dynamics, and interactions in daily activities.
This technique appears simple, but it is very powerful because it allows you to pick up on subtle signals that rarely emerge in formal meetings.ali.
4. Document analysis
Emails, meeting notes, tickets, deliverables, reports, retrospectives: every document tells a part of the project’s story.
Twproject, for example, centralizes all these materials, making it an ideal basis for continuous, easily traceable qualitative assessment.
5. Concept maps and journey maps
Concept maps and journey maps are highly effective visual tools for qualitative assessment because they clearly represent relationships, perceptions, obstacles, and expectations.
Concept maps are used to visualize the relationships between ideas, problems, roles, processes, or decisions.
In a qualitative assessment, they are helpful for:
- quickly representing what emerges from interviews and focus groups;
- highlighting discrepancies between the team’s vision and the stakeholders’ vision;
- identifying connections that might not emerge verbally;
- isolating recurring themes or latent critical issues;
- structuring diverse perceptions and viewpoints into a single framework.
Their value lies in transforming a set of comments and impressions into a readable map that allows the project manager to identify patterns and priorities.
A journey map is a representation of the “journey” of a user, customer, or stakeholder through the different stages of a process or project.
It is widely used in market research, but is equally valuable for project management. It can be constructed to analyze the customer’s journey, as well as those of the internal team and suppliers, identifying differences and alignment between what should happen (planned process) and what actually happens (real experience).ealmente accade (esperienza vissuta).
How to perform a qualitative assessment correctly: the operational guide
1. Define the objective of the analysis
Before starting a survey, it is essential to clarify what you want to understand:
- team satisfaction?
- uncalculated risks?
- customer perception of deliverables?
- the quality of internal processes?
Without a clear objective, the data collected risks being too generic.
2. Choose the most suitable methods
Quantitative methods are valuable, but here the goal is to analyze the qualitative dimension.
By choosing between interviews, observation, document analysis, or focus groups, the project manager can build a complete and coherent picture.
3. Collect information systematically
A qualitative assessment must be planned just as any other operational phase of the project.
Information can be gathered:
- during progress meetings
- using collaborative digital tools
- through internal surveys
- with facilitated discussions.
Twproject, by integrating activities, documents, and discussions, helps to ensure that critical information, which often forms the basis for more reliable qualitative assessments, is not lost.
4. Analyze data and identify patterns
A good qualitative assessment does not just report opinions, but highlights patterns:
- which critical issues are repeated?
- What perceptions differ between teams and stakeholders?
- Which priorities are perceived as urgent?
Here, the project manager plays an interpretative role, linking subjective information with operational objectives.
5. Compare qualitative and quantitative
It is essential to correlate numerical data and human feedback.
For example:
- if a task is behind schedule, KPIs explain by how much, while feedback explains why.
- if the budget is exceeded, the numbers show the extent, while interviews clarify the cause.
The combination of qualitative and quantitative data provides the most effective insights.e.
6. Present the results clearly
Once the analysis is complete, it is crucial to report concrete summaries:
- perceived risks,
- suggestions received,
- repeated critical issues,
- opportunities identified,
- proposals for improvement.
Dashboards and reports, such as those available in Twproject, also allow you to view qualitative information and turn it into easily shareable insights.
7. Use the results to improve the project
A qualitative analysis is useless if it does not lead to decisions.
For this reason, it must generate:
- corrective actions
- process reviews
- improvements in communication
- realignments between teams and stakeholders.
When qualitative assessment really makes a difference
Qualitative assessment is essential in the following cases:
- projects with many stakeholders and high emotional impact;
- innovative or experimental projects;
- conflictual situations;
- contexts with distributed teams or different cultures;
- critical phases such as start-up, release, or retrospective.
It is a decisive tool when the project manager needs to anticipate problems that the numbers do not yet show.
Why integrate tools such as Twproject into qualitative assessment
Twproject greatly facilitates the process because:
- it centralizes information, feedback, and documents;
- it allows you to monitor team sentiment through discussions and notes;
- it creates a digital history of the project that is useful for in-depth analysis;
- it integrates reports that help with the mixed interpretation of qualitative and quantitative data;
- it allows qualitative insights to be linked to operational activities.
This makes every qualitative assessment more comprehensive, transparent, and repeatable.




