Critical Chain vs Critical Path are two distinct project management methods..
Critical Chain is a new approach that is gaining popularity and challenging the traditional method, which relies on the Critical Path.
In this article, we’ll explore how they work, their differences, and which approach is best.
CONTENT
What is the Critical Chain Method (CCM)?
This approach focuses on identifying and managing critical resources within a project to optimize project planning, reduce delays, and improve completion on schedule.
Unlike the Critical Path method, which focuses on crucial operations based solely on duration and dependencies, the Critical Chain method also factors in resource availability.
One of the key elements of the Critical Chain methodology is buffer management to mitigate uncertainty-associated risks. There are three buffers:
· Project Buffer: included at the end of the project to absorb any delays accumulated during the work.
· Feeding Buffer: Included among non-critical activities to prevent any delays in secondary tasks from affecting the main path.
· Resource Buffer: Guarantees that resources are available at the right time. Yet another distinctive feature of Critical Path is the reduction of multitasking.
Many companies assign resources to more than one project or task at a time, which causes constant changes and a possible loss of productivity and efficiency.
With the Critical Path method, critical resources are focused on one task at a time, thus reducing the risks associated with multitasking.
This methodology provides benefits such as a greater probability of completing the project on schedule, a reduction in the total execution time, and better resource management.
What is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
The CPM, critical path method, is a project management technique used to determine the longest path of interdependent activities, thus establishing the minimum time needed to complete a project.
The Critical Path Method emerged as one of the most popular tools for project managers’ planning and monitoring activities.
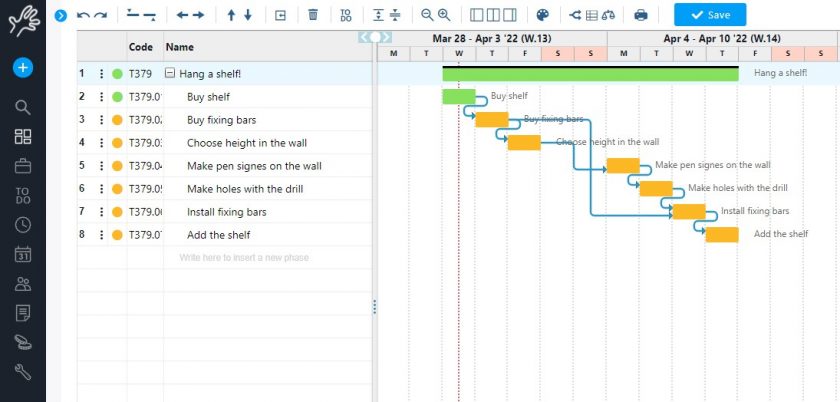
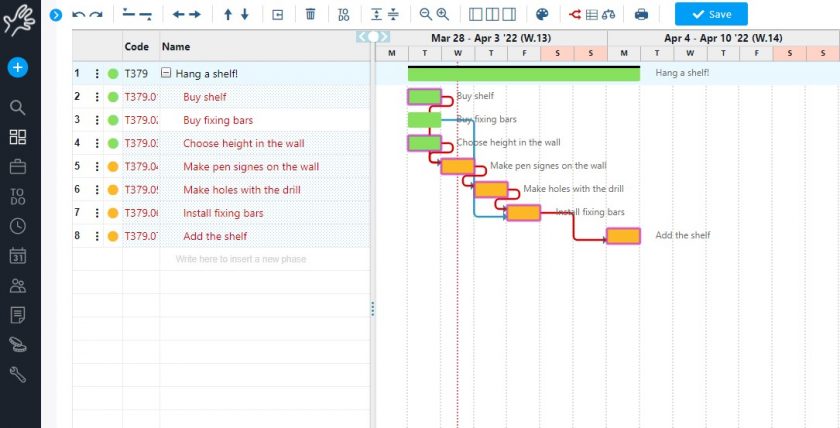
This method is based on constructing a network diagram that represents all the tasks necessary for completing a project, identifying their dependencies, and estimating the duration of each one.
The so-called critical path is the task sequence with the longest total duration, which determines the minimum duration for completing the project.
If any task on the critical path is delayed, the entire project will be delayed unless changes are made to the schedule.
In CPM, one of the core concepts is “float,” or margin of flexibility.
Total float indicates the maximum delay time allowed for an activity without impacting the project completion date.
On the other hand, free float indicates the delay time that an activity can undergo without influencing the start of a subsequent activity.
The CPM has many benefits: it allows you to identify critical activities to allocate resources accordingly, and it enables more accurate planning by identifying possible bottlenecks in advance.
Despite these strengths, the Critical Path Method does present some challenges.
For example, this methodology requires accurate data on activity duration, which is not always possible in highly uncertain environments.
Furthermore, the CPM does not take into account limitations related to resource availability, an aspect better managed by the Critical Chain methodology.
Differences between the Critical Chain Method and the Critical Path Method in project management
· Priority: The Critical Chain method focuses on resource and buffer management, while Critical Path focuses on task management.
· Resources: The Critical Path Method is less precise than the Critical Chain Method because it assumes that all resources will be accessible simultaneously. The CCM focuses on limited resources and uses accessible resources to create a feasible schedule.
· Buffer: As we saw in the Critical Chain method, the buffer is used for the whole project, while in the Critical Path method, the additional time is applied to single tasks.
· Multitasking: CPM supports multitasking, which means that two activities in the path can be completed simultaneously. On the contrary, CCM does not support multitasking.
Critical Chain vs Critical Path: using project management software
The use of project management software is crucial for effectively employing both the Critical Path Method (CPM) and the Critical Chain Method (CCM).
A project management tool allows you to improve resource planning, monitoring, and optimization.
One of the best project management software programs on the market is Twproject.
This tool allows you to automate the calculation of the critical path, visualize the progress of activities in real-time, and improve resource management, thus increasing the efficiency and probability of the project’s success.
Twproject perfectly adapts to both CPM and CCM methodologies. Specifically:
- With the Critical Path Method, Twproject provides features that allow you to create network diagrams, establish dependencies between activities, and thus identify the critical path. Thanks to these features, project managers can automatically estimate the minimum duration of the project and identify the activities that directly influence the completion date. Moreover, the real-time updating feature helps the team to monitor any delays and to intervene quickly to keep the project on track.
- For the critical chain method, using Twproject helps to manage critical resources and project buffers effectively. This tool allows you to allocate resources optimally, avoid multitasking, and ensure that crucial activities are completed without interruption. In addition, Twproject provides customized dashboards and reports to visualize buffers and promptly report any time overruns.
Between CCM and CPM, no method is objectively better than the other.
The best approach depends on various criteria, including the project, the team, and the corporate culture.
Independently of the method chosen, using project management software such as Twproject will increase the probability of success in project management and allow you to work more efficiently.